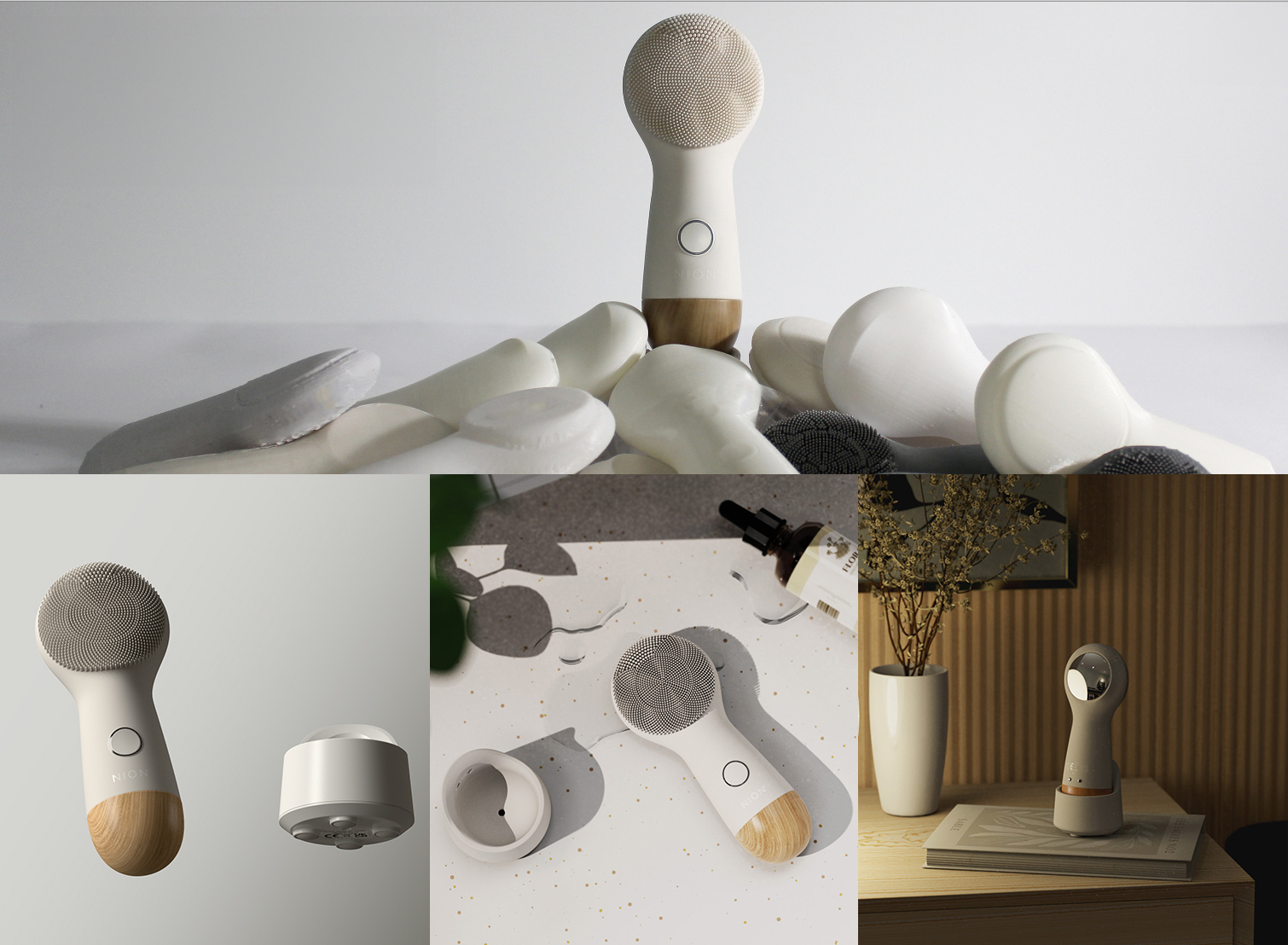
In the face of escalating climate change and environmental degradation, the significance of sustainable product design cannot be overstated. Businesses and inventors seeking to manufacture products must recognize the pressing need to embrace sustainability as an integral aspect of their operations. Sustainable products are no longer seen as a niche but as a necessity.
What we will cover:
- The Environmental Consequence of Product Design
- Market Demand for Manufacturing Sustainable Products
- What Is Sustainable Product Design and How to Implement it?
- The Future of Sustainable Product Design and Manufacturing
The Environmental Consequence of Product Design
- According to a comprehensive report by the World Economic Forum, projections indicate that the global population is poised to reach a staggering 9.7 billion individuals by the year 2050.
- Another study conducted by the World Bank shed light on the alarming trajectory of solid waste generation. Disturbingly, solid waste is estimated to skyrocket by a staggering 70% by 2050, resulting in a staggering annual production of 3.4 billion tons.
- The Global e-Waste Monitor 2020 unveiled that the world had generated an astounding record of 53.6 million metric tons of electronic waste in 2019 alone. Only 17.4% of this colossal amount was officially documented as being properly recycled, signaling an urgent need for more sustainable approaches to electronic waste management.
Market Demand for Manufacturing Sustainable Products
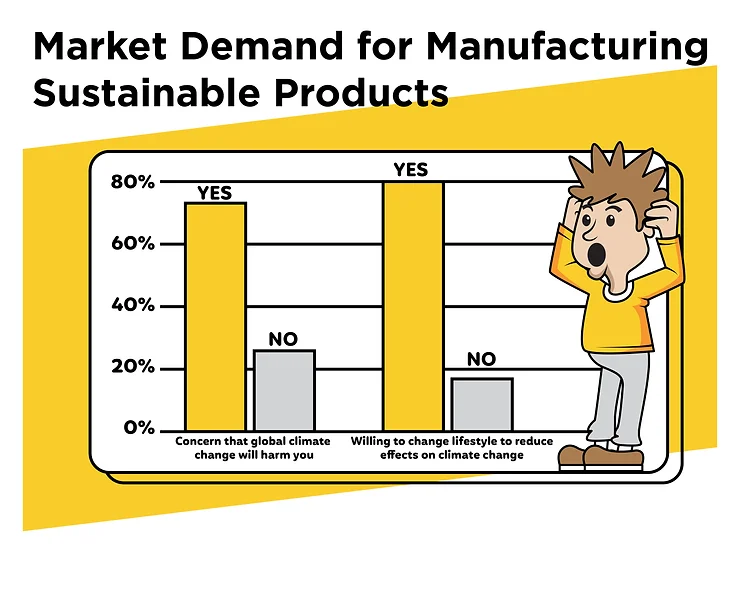
Will considering sustainability increase sales? The good news is that the demand for sustainable product design is growing. According to a survey by the Global Buying Green Report, 83% of consumers said they would be willing to pay more for products made from sustainable materials. For instance, Deloitte’s Global State of the Consumer Tracker reveals that a significant proportion of consumers are embracing sustainable products. In April 2023, 46% of consumers across 23 countries purchased at least one sustainable good or service. Not to mention, according to a study by Vicente-Molina, Fernández-Sáinz, and Izagirre-Olaizola (2013), consumers’ opinion on green marketing was initially influenced by feelings of guilt, leading to purchases driven by guilt. However, Paddy Dolan (2014), a researcher from the Dublin Institute of Technology, argued that emotions play a crucial role in the intention to purchase green products. Today, current statistics suggest a shift in consumer mindset, where the feeling of responsibility empowers them as consumers. This shift has resulted in a more positive opinion of green marketing overall. It’s important to note that this demand extends beyond a niche group of young, affluent climate activists, demonstrating a broader appeal for green products among the general audience. What Is Sustainable Product Design and How to Implement it?

In order to effectively implement sustainable product design, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of the entire product life cycle, encompassing the design stage, manufacturing process, and eventual disposal.
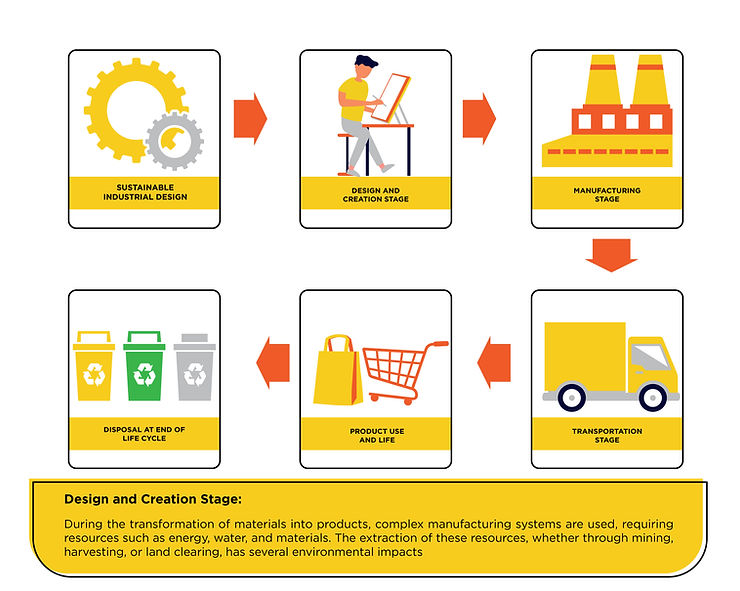
Design and Creation Stage: During the transformation of materials into products, complex manufacturing systems are used, requiring resources such as energy, water, and materials. The extraction of these resources, whether through mining, harvesting, or land clearing, has several environmental impacts:
- Carbon Emissions: The process generates carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, contributing to climate change.
- Resource Use: It involves the consumption of water and land resources.
- Waste Generation: Manufacturing produces waste products that need to be managed properly.
Manufacturing Stage: The primary environmental impact of manufacturing is related to the energy used in the production process and the emissions (air, water, and waste) generated during this stage.
Transportation Stage: Transportation contributes to carbon dioxide emissions, which is a significant driver of climate change. The weight and space utilization of products during transportation are key concerns. Road and air transportation generally have a larger impact compared to sea or rail transportation.
Product Use and Life:
- Quality: Using suitable materials and manufacturing processes can increase product durability, reducing the need for disposal and replacement.
- Function and Efficiency: Convenient and effective products are less likely to be replaced by competing alternatives.
- Appearance: If the product’s aesthetics are based on a passing trend, it may be replaced even if it is durable.
- Additional resources: Other materials required for the product’s functionality, such as cleaners, covers, attachments, or necessary services throughout its lifespan.
Disposal at End of Life Cycle: Consider the product’s fate at the end of its life cycle, whether it will end up in landfill or be recycled. While you cannot control customer behavior, eco-design can facilitate recycling and minimize the environmental impact of landfill disposal.
- Design for Easy Recycling: Make components that need to be discarded (e.g., packaging) easy to recycle.
- Avoid Landfill Impact: Prevent organic materials like wood from going to landfill, as they can produce methane, a potent greenhouse gas when they decompose without exposure to oxygen.
The Future of Sustainable Product Design and Manufacturing
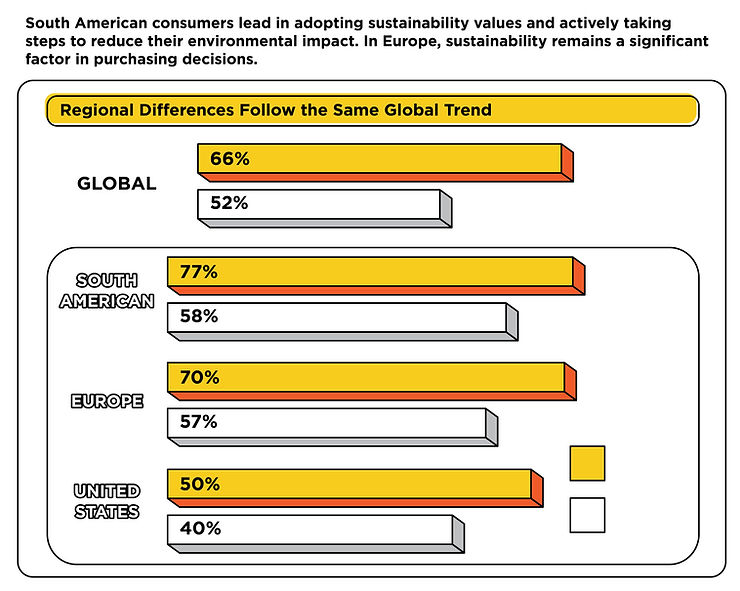
According to a study by Accenture, 94% of CEOs believe that sustainability is important for the future success of their companies. This highlights the recognition among business leaders that sustainability, including sustainable product design, is crucial for long-term viability and competitiveness. Additionally, a study by Straits Research found that the market for sustainable packaging is expected to reach $409 billion by 2030, driven by increasing consumer awareness and demand for eco-friendly products.
Furthermore, governments and businesses are also recognizing the importance of sustainable product design. The European Union has implemented the Circular Economy Action Plan, which aims to transition the EU towards a more sustainable and circular economy. This includes supporting the development of sustainable products and services and promoting the use of sustainable materials.
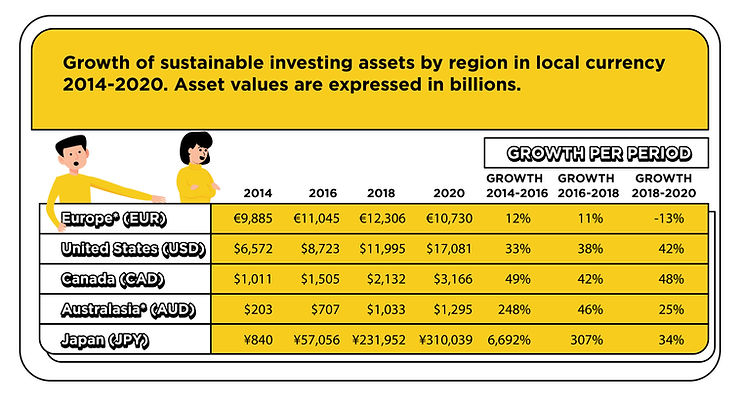
The Global Sustainable Investment Alliance reported that global sustainable investment assets reached $35.3 trillion in 2020, a 15% increase from 2018. This demonstrates the growing interest and financial backing for sustainable initiatives, including sustainable product design.
If you’re seeking to integrate sustainable design or gain further insights into sustainable manufacturing, we invite you to connect with our exceptional team of experts at Gizmospring. Feel free to explore our range of services and discover our portfolio. We are dedicated to providing innovative solutions that align with sustainable practices and contribute to a greener future.