Staying updated with industry trends is extremely important for success in product design and manufacturing. As we progress through 2024, three significant shifts dominate the field:
- An emphasis on sustainability and the circular economy
- The integration of advanced technology
- A focus on mass customization
But how can businesses utilize these trends to maintain a competitive edge in an evolving market? This article will explore these key trends, delving into their influence on the product design and manufacturing industry.
An Emphasis on Sustainability and the Circular Economy
What is Circular Economy in Design?

The circular economy is an economic system aimed at eliminating waste and the continual use of resources. It contrasts with the traditional linear economy, which has a ‘take, make, dispose’ model of production. In a circular economy, resources are kept in use for as long as possible, extracting the maximum value from them while in use, then recovering and regenerating products and materials at the end of each service life.
Examples of Sustainable Materials and Processes Being Adopted in Product Design and Manufacturing
Businesses across various sectors are increasingly incorporating sustainable materials and processes into their operations. For instance, biodegradable plastics derived from plant-based materials are being used to reduce dependency on fossil fuels. In manufacturing, processes like modular design and precision manufacturing help reduce waste by enhancing the efficiency of resource use. Another example is the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to drive production processes, minimizing carbon footprints.
The Role of Design in Enhancing Product Longevity and Recyclability
Design plays a huge role in the circular economy by optimizing product life cycles for greater reuse and recycling. Designers are now focusing on creating products that are easier to repair, upgrade, and disassemble. For example, designing consumer electronics with modular components allows consumers to replace or upgrade specific parts instead of the entire device, thus extending the product’s lifespan and reducing e-waste.
Similarly, incorporating standardized components can simplify the recycling processes, ensuring that materials can be effectively separated and reused at the end of the product’s life. Through these approaches, design not only contributes to sustainability but also enhances economic viability by aligning products with the principles of the circular economy.
The Integration of Advanced Technology
What are Digital Twins in Manufacturing?
Digital twin technology involves creating a digital replica of a physical entity, enabling real-time monitoring, testing, and assessment. This technology is an innovation within modern manufacturing environments, as it allows manufacturers to simulate processes and products without the physical risks or costs associated with a tangible model. By using digital twins, companies can make more informed decisions, enhance product quality, and accelerate the development cycle, significantly reducing time-to-market. These benefits not only streamline manufacturing operations but also encourage innovation and efficiency across various industries.
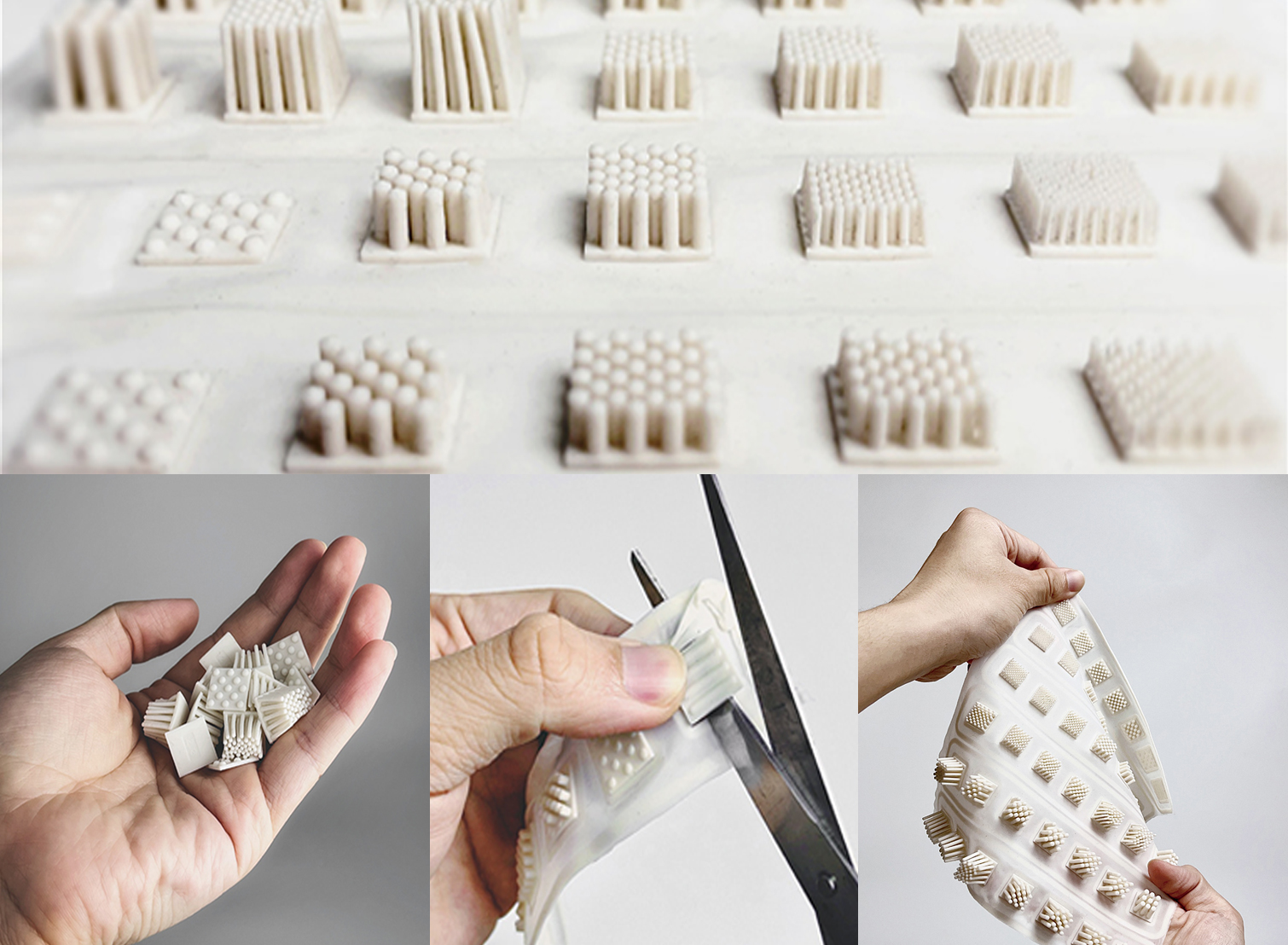
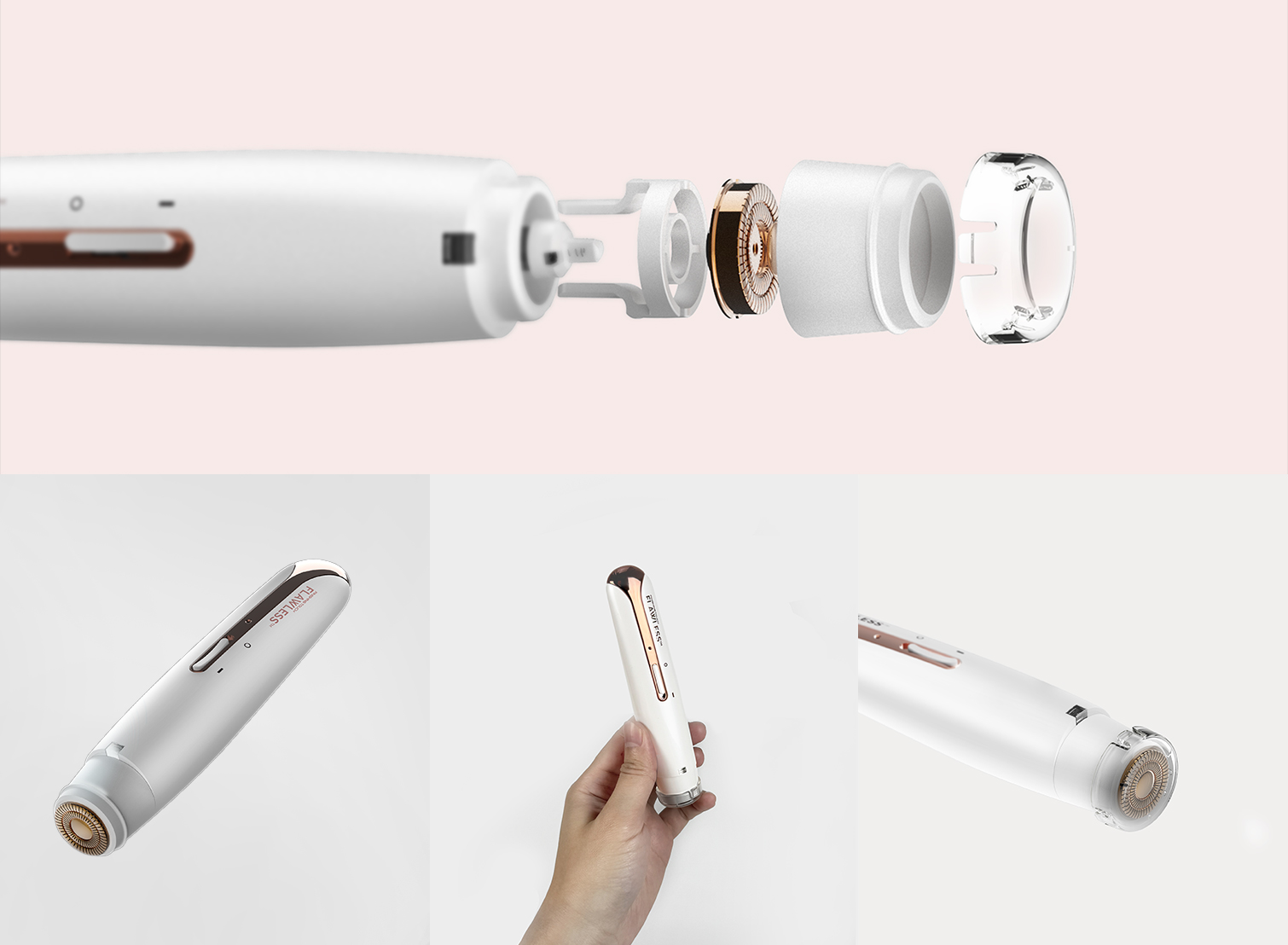
Emergence of Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, has transcended its initial status as a prototyping tool and is now a vital part of production across many sectors. This technology allows for greater customization, reduces material waste, and offers significant time savings in product development and manufacturing.
Impact on Design and Production:
- 3D printing technologies enable the production of complex geometric structures that were previously impossible or too costly to achieve, opening new avenues for product design and innovation.
- The ability to manufacture on-demand reduces the need for large inventories and streamlines supply chains, which is particularly crucial in industries such as healthcare and automotive where customization and speed are critical.
A Focus on Mass Customization

What is Mass Customization?
In today’s market, customization is no longer a luxury—it’s a growing expectation among consumers. The ability to personalize products according to individual preferences has become a prominent trend, gaining significant traction across multiple sectors, from automotive to consumer electronics. This shift towards mass customization is directly linked to advancements in technology and changes in consumer behavior, which increasingly demand more tailored products and experiences.
Personalization Through Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
Technologies such as additive manufacturing (3D printing) and CNC machining have revolutionized how products can be customized. These methods allow for intricate designs and modifications that were either impossible or prohibitively expensive with traditional manufacturing techniques. For instance, 3D printing enables the production of parts and products that are specifically designed to fit individual specifications without the need for expensive tooling or setup changes.
Software and AI-Driven Customization
Software solutions and AI are playing pivotal roles in enabling mass customization. Companies utilize AI to analyze customer data and preferences, which in turn informs the design process to create highly personalized products. For example, in the fashion industry, AI algorithms can suggest custom clothing sizes for consumers based on their browsing history and past purchase data, ensuring a better fit and higher satisfaction.
Modular Design and Interchangeable Parts
Modular design is another approach facilitating customization. Products designed with interchangeable parts allow consumers to modify or upgrade certain aspects without replacing the entire product. This is evident in the electronics industry, where some smartphones and laptops are designed to enable users to upgrade memory or swap out batteries easily, thus extending the product’s life and adapting to user needs.
Customer Involvement in the Design Process
Businesses are increasingly involving customers directly in the design process. Through interactive online platforms, customers can select colors, features, and components to assemble a product that meets their specific requirements. This direct involvement not only enhances customer satisfaction but also promotes a deeper connection between the consumer and the brand.
Impact on Supply Chains and Retail
The rise in customization has significant implications for supply chains and retail strategies. Manufacturers need to adapt their operations to handle a variety of custom orders efficiently, which may involve more sophisticated logistics and inventory management systems. Retailers, both online and offline, must align their offerings and marketing strategies to highlight the availability and benefits of customized products.
Conclusion
The product design and manufacturing landscape in 2024 is undergoing significant transformations due to:
- Manufacturers are rethinking production cycles to reduce waste and maximize resource reuse, aligning with sustainability goals.
- Digital twins and additive manufacturing are boosting efficiency, enabling rapid prototyping, and shortening time-to-market, redefining possibilities in product development.
- Rising consumer demand for personalized products is reshaping expectations and pushing manufacturers towards more flexible and innovative design approaches.
As these trends evolve, the ability to adapt and innovate becomes crucial for businesses striving for success. The ongoing integration of these trends promises new challenges and opportunities for growth in product design and manufacturing.