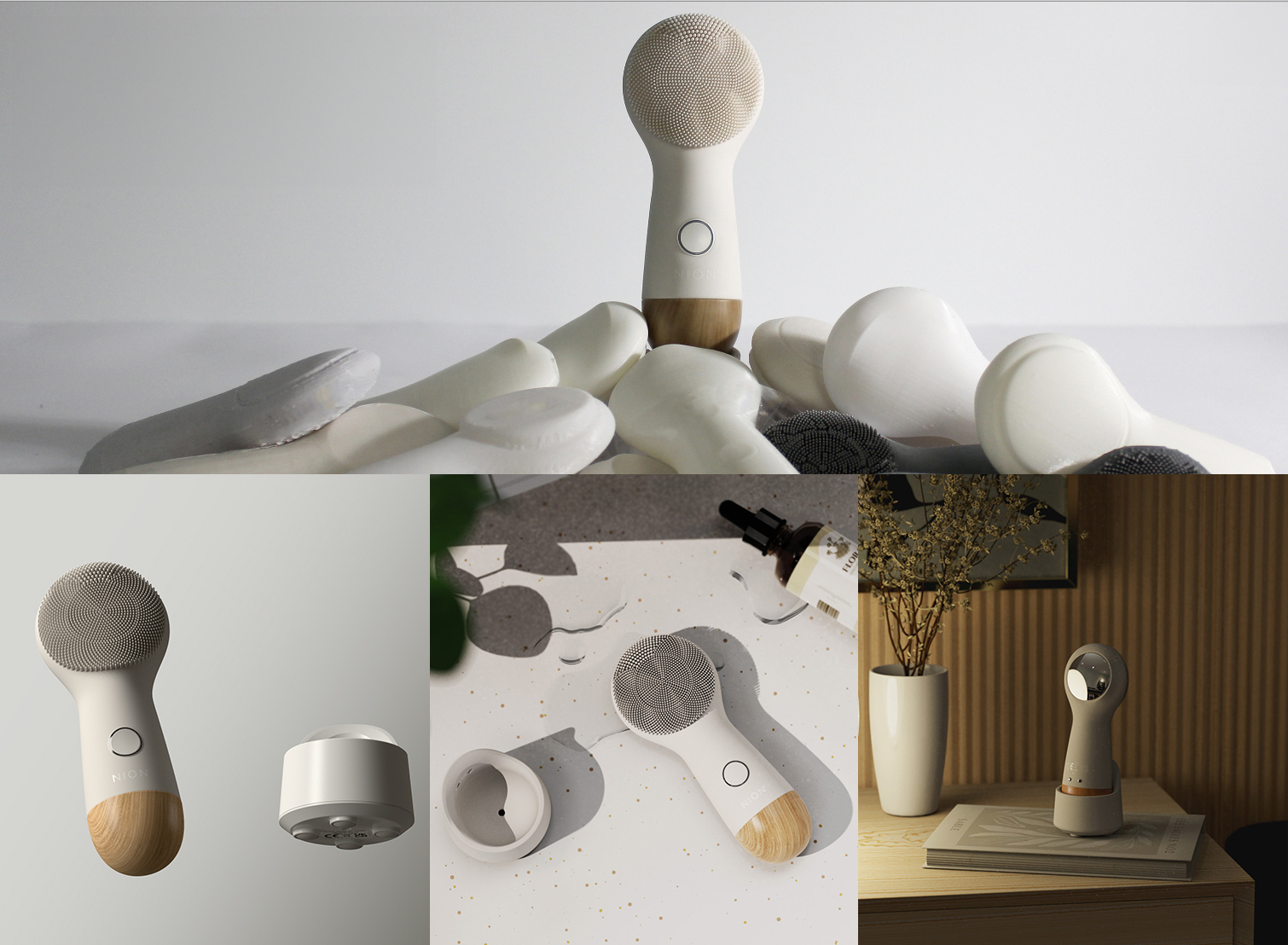
Offshore manufacturing offers businesses access to skilled labor markets and established supply chains abroad. As of 2025, companies are increasingly evaluating the decision between manufacturing locally in the U.S. or offshore, particularly in China, where robust production infrastructures can enhance efficiency and scalability.
However, this decision goes beyond logistical advantages. While offshore manufacturing in China provides opportunities for scaling and efficiency, domestic production in the U.S. offers better quality control, quicker lead times, and stronger IP protection. This article breaks down the key pros and cons of offshore manufacturing to help businesses make informed decisions, focusing on finding the right supplier and balancing operational needs with quality.
What is Offshore Manufacturing?
Offshore manufacturing refers to the practice of relocating the production or assembly of goods to another country, typically to benefit from lower labor costs, increased production capacity, or access to specialized skills and resources. Companies often move manufacturing operations overseas to reduce operating expenses, streamline supply chains, and maintain competitive pricing in their home markets. The goal is to produce goods more efficiently while capitalizing on the advantages that foreign markets may offer in terms of cost and infrastructure.
Globalization has played a crucial role in the rise of offshore manufacturing. As international trade barriers have decreased and global supply chains have matured, businesses are now able to source materials, labor, and production facilities from virtually any part of the world. China has become a central player in this process, emerging as a manufacturing powerhouse due to its combination of low labor costs, extensive infrastructure, and mature supply chains. This makes it one of the most attractive destinations for offshore manufacturing today, particularly for companies seeking to balance cost savings with large-scale production capabilities.
The Pros of Offshore Manufacturing in 2025

1. Lower Production Costs
Labor Costs: One of the most significant advantages of offshore manufacturing is the lower labor costs, especially in China. Chinese labor is typically 1/3 to 1/4 the cost of U.S. labor, enabling companies to reduce production expenses significantly. Other countries like Vietnam and Thailand also offer similarly low labor costs, making them attractive alternatives. For example, labor costs in Vietnam can be as little as one-tenth of U.S. labor, providing significant savings.
Cheaper Raw Materials: Manufacturing in China also brings businesses closer to the source of many essential raw materials. This proximity helps reduce the costs associated with sourcing and transporting materials, leading to faster production times and lower overall expenses. For industries like electronics and textiles, where raw materials are often sourced from within Asia, this can make a substantial difference in lead times and cost efficiency.
2. High-Volume Capacity and Scalability
Production Scalability in China: Chinese factories are well-equipped to handle large-scale production, making it easy for businesses to increase their output as demand grows. Many manufacturers offer volume discounts, making large orders more cost-effective. This scalability is crucial for companies looking to expand quickly while maintaining cost control.
3. Established Supply Chains
China’s Mature Supply Chain Infrastructure: China’s well-established supply chain infrastructure ensures that manufacturers have access to a reliable flow of raw materials, reducing the risk of delays. Whether it’s electronics, textiles, or heavy machinery, Chinese manufacturers benefit from mature and efficient supply chains that streamline the production process.
4. Availability of Skilled Labor
Specialized Workforce: China has a deep pool of highly skilled labor, including engineers, designers, and technicians with expertise across a wide range of industries. For companies that require complex manufacturing processes, such as electronics or medical devices, China offers the necessary talent to meet these advanced production needs. This skilled workforce, combined with cost savings, makes offshore manufacturing in China a compelling option for many businesses.
The Cons of Offshore Manufacturing in 2025
1. Higher Shipping Costs and Lead Times
Shipping from China to the U.S.: One of the biggest challenges of offshore manufacturing is the cost and time involved in shipping products across long distances. Shipping goods from China to the U.S. can be costly due to rising freight rates, tariffs, and import duties. Additionally, longer transit times increase the risk of delays, which can disrupt supply chains and make it harder to meet customer demand.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: The COVID-19 pandemic exposed the fragility of global supply chains, especially those dependent on offshore manufacturing. Disruptions in production, shipping, and customs delays highlighted the risks of relying heavily on distant suppliers. Companies need to consider the potential for future disruptions when evaluating offshore manufacturing options.
2. Lack of On-Site Oversight
Quality Control Challenges: When manufacturing overseas, it can be difficult to ensure product quality without being physically present at the factory. Miscommunication between manufacturers and buyers can lead to mistakes in production, such as incorrect materials, inconsistent quality, or missed deadlines. Without direct oversight, resolving these issues can be challenging and time-consuming.
The Importance of Having a Local Representative: To mitigate these risks, partnering with a local representative or agent can help ensure better communication and oversight. A local representative can conduct factory visits, perform quality control checks, and address issues as they arise, reducing the potential for costly errors.
3. Language and Cultural Barriers
Communication Challenges: Working with manufacturers in China can present challenges due to language differences and cultural norms. Misunderstandings in negotiations, product specifications, or timelines can occur if there isn’t clear communication. Additionally, cultural differences in business practices can sometimes lead to delays or unexpected changes in production.
4. Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Risk of IP Theft in China: While offshore manufacturing can provide cost savings, it also comes with risks to intellectual property. China has a reputation for weaker enforcement of IP laws compared to other countries, raising concerns about copycat products or unauthorized use of proprietary designs. This is a critical concern for businesses producing innovative or patented products.
5. Customer Service Challenges
Delayed Response and Support: Customer service can be another challenge when working with overseas manufacturers. Time zone differences, language barriers, and distance can lead to delays in communication when issues arise with product quality or delivery. For example, if a batch of goods does not meet standards or shipping is delayed, resolving these problems can take longer and impact customer satisfaction.
U.S. Manufacturing: Is It Worth It?

1. Higher Labor and Operating Costs
Manufacturing in the U.S. is generally more expensive than offshore alternatives, primarily due to higher labor, regulatory, and tax costs. American workers receive significantly higher wages compared to their counterparts in China, Vietnam, or Mexico, making labor one of the largest expenses for U.S.-based manufacturers. Additionally, businesses must adhere to stringent regulatory requirements related to environmental standards, workplace safety, and employment laws, all of which contribute to higher operational costs. Tax rates, while reduced by recent reforms, also remain higher compared to many offshore locations, further increasing the cost of production.
However, these added expenses are often balanced by improved oversight and quality control. U.S. manufacturers tend to offer more direct involvement in the production process, reducing the risk of errors or miscommunications and ensuring that products meet strict quality standards from the outset.
2. “Made in USA” Branding Value
For certain industries, particularly those focused on premium goods or industries with a consumer base that values local sourcing, the “Made in USA” label can provide a competitive edge. Many American consumers, especially in sectors like health, wellness, food, and certain high-tech goods, are willing to pay a premium for products that are manufactured domestically. This is especially true for businesses that prioritize sustainability, fair labor practices, or craftsmanship. The “Made in USA” label carries a sense of trust, quality, and social responsibility, which can be an important selling point for many companies.
Moreover, U.S. manufacturers are often associated with high standards for safety, environmental responsibility, and quality, all of which can enhance a brand’s reputation.
3. Proximity to the Consumer Market
One of the biggest advantages of manufacturing in the U.S. is proximity to the consumer market. Shorter shipping times mean faster delivery to U.S. customers, which is increasingly important in today’s competitive e-commerce and retail landscapes, where customers expect rapid fulfillment. Additionally, companies can avoid international shipping fees, tariffs, and potential delays at customs, which can be costly and time-consuming for offshore operations.
Having production closer to home also allows businesses to be more responsive to market demands and make adjustments to production in real-time. This flexibility can be a major advantage for businesses that prioritize agility, especially when launching new products or reacting to shifts in consumer preferences.
In summary, while U.S. manufacturing comes with higher costs, it also offers valuable benefits such as greater quality control, faster time-to-market, and enhanced branding opportunities for companies that can leverage the “Made in USA” label. For businesses prioritizing local markets and premium positioning, manufacturing in the U.S. can be well worth the investment.
China Manufacturing: Is It Worth It?
1. Lower Costs and Higher Production Volume
Cost Efficiency: Manufacturing in China remains one of the most cost-effective options available, particularly for businesses looking to scale quickly. Labor costs in China are significantly lower than in the U.S., with savings ranging from 60% to 75%. Beyond labor, raw materials and supply chains are often more affordable, allowing businesses to maintain competitive pricing and increase their profit margins.
High Production Volume: China’s manufacturing infrastructure is well-equipped to handle large-scale orders, making it easier for businesses to ramp up production to meet demand. Chinese manufacturers excel at scaling production efficiently, which is especially advantageous for companies entering high-demand markets where rapid production is key.
2. Access to Specialized Expertise and Technology
Manufacturing Expertise: China has a wealth of specialized industries, particularly in electronics, textiles, and consumer goods. With highly skilled engineers, designers, and technicians, businesses can access top-tier manufacturing capabilities at a fraction of the cost compared to U.S. manufacturers. Whether the need is for high-precision engineering or mass production, Chinese manufacturers can deliver high-quality products efficiently.
Advanced Manufacturing Technology: Many Chinese factories are equipped with state-of-the-art manufacturing technology, enabling high-precision production and the use of specialized materials. This advanced technological capability is especially crucial for businesses producing complex products such as electronics, medical devices, or innovative consumer goods.
3. Mature Supply Chain Infrastructure
Established Supply Chains: China’s mature supply chain network provides easy access to raw materials, components, and other production necessities, reducing delays and keeping costs low. For businesses with intricate supply needs, China’s well-developed infrastructure ensures efficient sourcing and faster time to market, making it an attractive option for complex manufacturing.
4. Risks with IP Protection and Quality Control
Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns: One of the major risks of manufacturing in China is the potential for intellectual property theft. Although China has made strides in improving IP law enforcement, concerns over counterfeiting and unauthorized production remain, particularly for businesses with proprietary or patented products.
Quality Control Challenges: Ensuring consistent product quality can be challenging when manufacturing overseas, especially without direct oversight. Miscommunication, cultural differences, and a lack of on-site quality control can lead to production issues. Businesses can mitigate these risks by working with trusted partners or hiring local representatives to oversee the manufacturing process.
5. Global Market Access and Lower Shipping Costs
Proximity to Asian and European Markets: Manufacturing in China offers a strategic advantage for businesses targeting global markets. China’s proximity to other major consumer regions, such as Asia and Europe, results in lower shipping costs for international distribution compared to U.S. manufacturing. This makes China an ideal base for businesses looking to expand globally.
Competitive Pricing with Faster Production: The efficiency of Chinese manufacturing processes, coupled with reduced costs, allows businesses to maintain competitive pricing while meeting market demand more quickly. This agility is particularly beneficial for companies in fast-moving industries where speed-to-market is critical for success.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between U.S. and Offshore Manufacturing
1. Cost vs. Quality
When deciding between U.S. and offshore manufacturing, the balance between cost savings and product quality is critical. Offshore manufacturing in China offers significant cost advantages, especially in terms of labor and raw materials, but it can also introduce risks related to product quality. In contrast, U.S. manufacturing generally ensures stricter quality control and adherence to regulations, albeit at a higher cost. Businesses must weigh the potential for cost savings in China against the possible need for additional quality control measures to maintain production standards.
2. Supply Chain Complexity
Offshore manufacturing involves managing a longer and more complex supply chain, which includes navigating international shipping, tariffs, and potential delays. This can complicate logistics and increase lead times, particularly when shipping from China to the U.S. In contrast, U.S. manufacturing offers a more streamlined process with shorter shipping times and easier market access, which can be beneficial for companies that prioritize speed and reliability in their supply chain.
3. Scalability Needs
For businesses that need to rapidly scale production, offshore manufacturing—especially in China—can be more advantageous. China’s factories are well-equipped to handle large-volume orders and can quickly ramp up production to meet growing demand. U.S. manufacturers may struggle to scale at the same speed or offer the same cost advantages, making offshore options more appealing for companies expecting significant growth.
4. IP Protection Concerns
One of the major concerns with offshore manufacturing, particularly in China, is the risk of intellectual property (IP) theft. To mitigate this risk, businesses should implement strategies such as using non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), carefully vetting suppliers, and working with trusted partners who have a strong track record of protecting IP. Additionally, companies can consider retaining control over certain key aspects of the production process or working with manufacturers that offer in-house development to reduce the chances of IP leakage.
In summary, choosing between U.S. and offshore manufacturing involves weighing cost savings against potential risks, particularly in terms of quality, supply chain complexity, scalability, and intellectual property protection.
When to Consider a New Manufacturing Partner
Working with the right manufacturing partner is essential for maintaining production quality and meeting deadlines. However, if you notice recurring delays, declining product quality, or communication breakdowns, it may be a sign that it’s time to reassess your partnership. Lack of transparency in processes, increased costs without added value, or persistent IP concerns are also red flags. Addressing these issues early can prevent further disruptions to your supply chain and protect your business.
For a more in-depth look, check out our article on Signs You Need a New Manufacturing Partner.
How to Find the Right Offshore Manufacturing Partner in 2025
Supplier Vetting Process
Finding the right offshore manufacturing partner requires thorough research and a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process:
Step 1: Research and Shortlist Suppliers
Begin by researching potential manufacturers through trusted online platforms like Alibaba, Global Sources, or Made-in-China. These platforms allow you to filter suppliers based on product categories, customer reviews, and company size.
Step 2: Check Certifications
Verify the supplier’s certifications and standards. For example, check for ISO (International Organization for Standardization) certifications, which ensure quality management systems, and look for industry-specific credentials, such as FDA approval for medical devices. This will help you confirm the manufacturer’s compliance with industry regulations and quality standards.
Step 3: Factory Visits
If possible, arrange a factory visit or hire a local representative to do it on your behalf. Seeing the facility firsthand helps you assess the factory’s production capabilities, equipment, and quality control processes. Virtual factory tours, where available, can also provide valuable insights.
Step 4: Request Samples and Quotes
Request product samples to evaluate the manufacturer’s capabilities and product quality. Obtain detailed quotes that break down costs, including production, shipping, and potential tariffs.
Step 5: Conduct Due Diligence
Before committing, conduct due diligence by checking the supplier’s reputation. Look for reviews, customer testimonials, and business ratings. Use resources like Dun & Bradstreet to assess the supplier’s financial stability and reliability.
Final Thoughts: A Balanced Approach to Offshore Manufacturing
While offshore manufacturing in China offers significant cost advantages, there are viable alternatives that combine affordability with high-quality production. Some suppliers utilize a unique model where they maintain their own factories in China, allowing them to uphold U.S. quality standards while benefiting from the cost savings of offshore manufacturing.
These suppliers stand out by bridging communication gaps with multilingual English-speaking teams, ensuring smooth coordination throughout the production process. Additionally, they implement strict quality control measures, often aligning with American standards such as the use of FDA-approved and medical-grade materials. This approach ensures that product quality is not compromised despite the offshore location.
Although this model may come with a slightly higher price tag compared to working solely with Chinese-based manufacturers, it remains a cost-effective alternative to domestic production while still delivering exceptional product quality. Moreover, when it comes to intellectual property (IP) protection, these suppliers offer a distinct advantage. By vertically integrating their operations—handling everything from product design to manufacturing—they minimize the need for outsourcing and ensure your IP remains protected.
Let’s Chat About Your Manufacturing Needs
Gizmospring adheres to US quality standards while being strategically located closer to the supply chain in Asia. This positioning ensures consistent product quality while offering significant cost savings compared to most US-based manufacturers. Additionally, Gizmospring practices Joint Development Manufacturing (JDM), collaborating with you from concept to final production, ensuring tailored solutions that meet your unique requirements.
Contact us to learn how we can help you achieve this balance.
FAQ
- What does it mean to offshore manufacturing?
Offshore manufacturing refers to relocating the production or assembly of goods to another country, usually to take advantage of lower labor costs, specialized skills, or increased production capacity. This strategy is often used to reduce operating expenses while maintaining competitive pricing. - What is offshoring production?
Offshoring production involves moving the entire manufacturing process or certain parts of it to a foreign country. Companies may choose offshoring to cut costs, access skilled labor, or streamline supply chains in markets where certain materials or expertise are more readily available. - What is an offshore product?
An offshore product is a good that has been manufactured or assembled in a foreign country, typically in regions where labor and production costs are lower. Companies often choose offshore production for items like electronics, textiles, and consumer goods to save on costs and increase scalability. - What is the difference between a source factory and an offshore factory?
A source factory is the original facility where a product is designed and often initially produced, usually closer to the home market. An offshore factory, on the other hand, is located abroad and is primarily used for large-scale production to reduce costs, leveraging cheaper labor and established supply chains. - What are the pros of offshore manufacturing in 2025?
The primary advantages include lower labor and production costs, access to a large pool of skilled labor, scalability, and well-established supply chain infrastructure in regions like China. Offshore manufacturing can also offer businesses greater flexibility when it comes to scaling up operations. - What are the cons of offshore manufacturing in 2025?
The main downsides include higher shipping costs, longer lead times, potential quality control challenges, intellectual property risks, and language or cultural barriers that can complicate communication and logistics. - How do I choose between U.S. and offshore manufacturing?
The decision comes down to balancing cost savings with quality control and supply chain complexity. Offshore manufacturing offers significant cost advantages, but U.S. manufacturing may provide better oversight, faster delivery times, and stronger IP protection. You should weigh these factors based on your business’s priorities. - What are the key factors to consider when selecting an offshore manufacturing partner?
When choosing an offshore manufacturing partner, consider factors like the supplier’s certifications, production capacity, quality control processes, and communication abilities. It’s also important to visit the factory, request samples, and check the supplier’s reputation before committing. - What should I look for in a good offshore manufacturing partner?
A reliable partner will have the right certifications, strong communication capabilities, and a good reputation in the industry. They should also be able to provide product samples and transparency in their manufacturing processes, ensuring quality and consistency. - When should I consider switching to a new manufacturing partner?
If you experience recurring issues like delayed production, poor quality control, or miscommunication, it may be time to reassess your current partnership. Lack of transparency, increasing costs without added value, and ongoing IP concerns are also red flags. For more details, check our article on Signs You Need a New Manufacturing Partner. - How do I communicate effectively with overseas suppliers?
Clear and concise communication is key. Use written documentation, visual aids, and ensure all specifications are outlined. Regular check-ins, understanding cultural differences, and possibly working with a local sourcing agent can help bridge communication gaps.