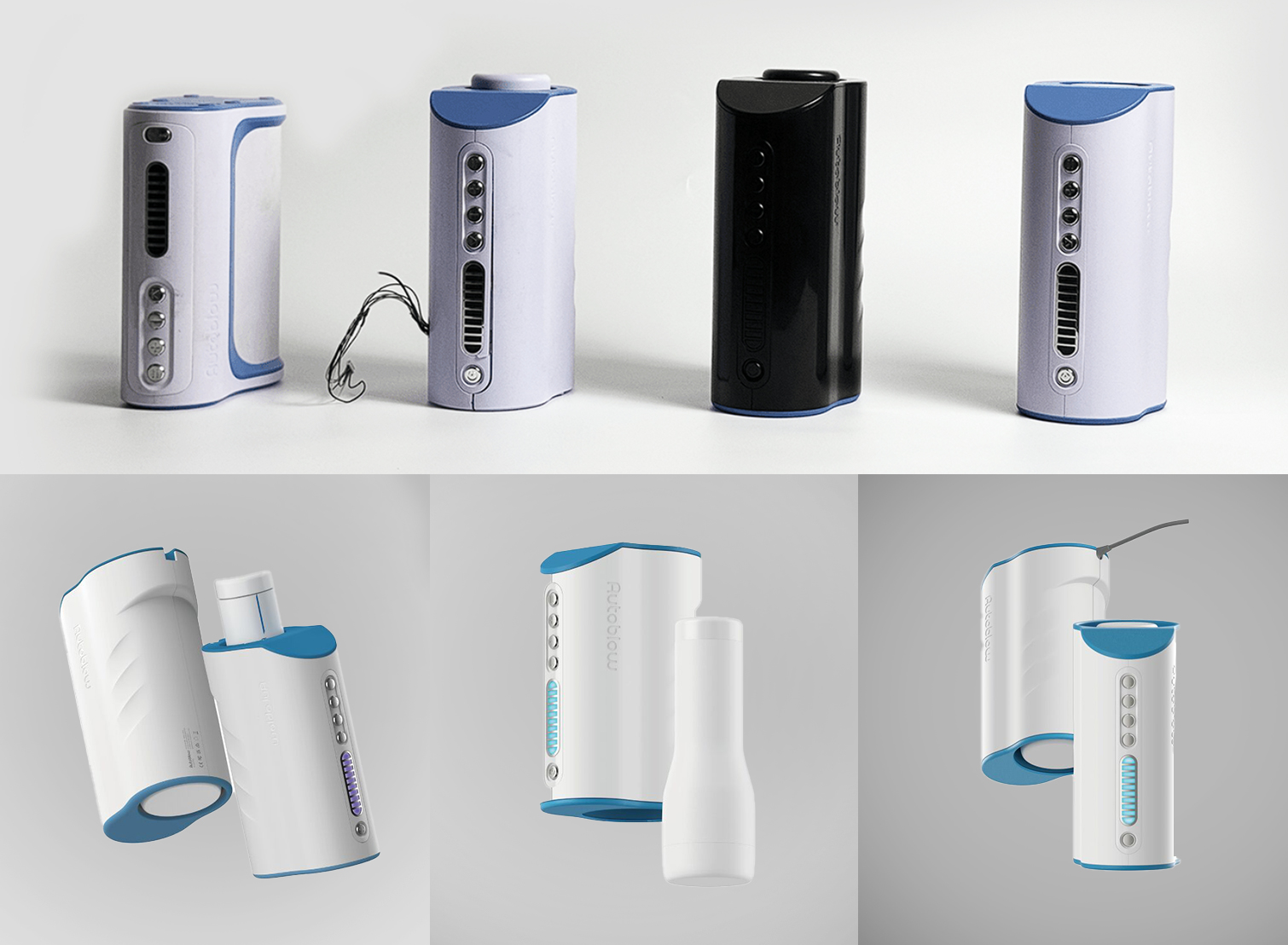
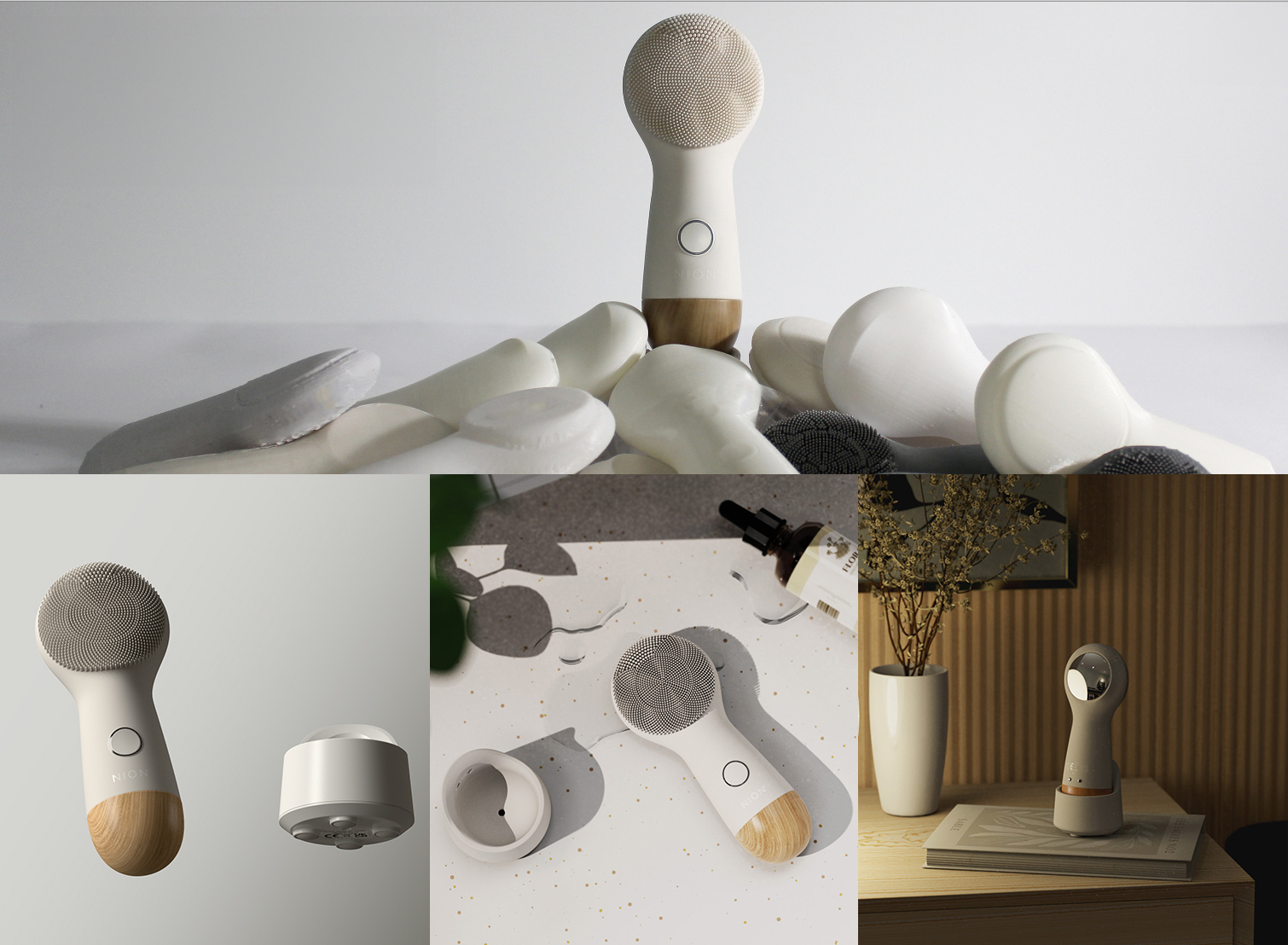
The evolution of industrial design has always mirrored the ever-changing demands of the consumer market. Today, one of the most profound shifts we’re observing is the transition from single-use, disposable products to modular designs. But what does this mean from an industrial design perspective, and how are manufacturers adapting?
This article will cover:
What is Modular Design?
Modular design refers to the creation of products that are composed of interchangeable parts or modules. This approach allows users to customize and modify their products with ease, aligning perfectly with the growing demand for personalization in the consumer market. By enabling the addition, removal, or replacement of individual components, modular design empowers consumers to tailor their products to fit their specific needs and preferences, enhancing user experience and satisfaction.
Personalization in Modern Consumer Markets
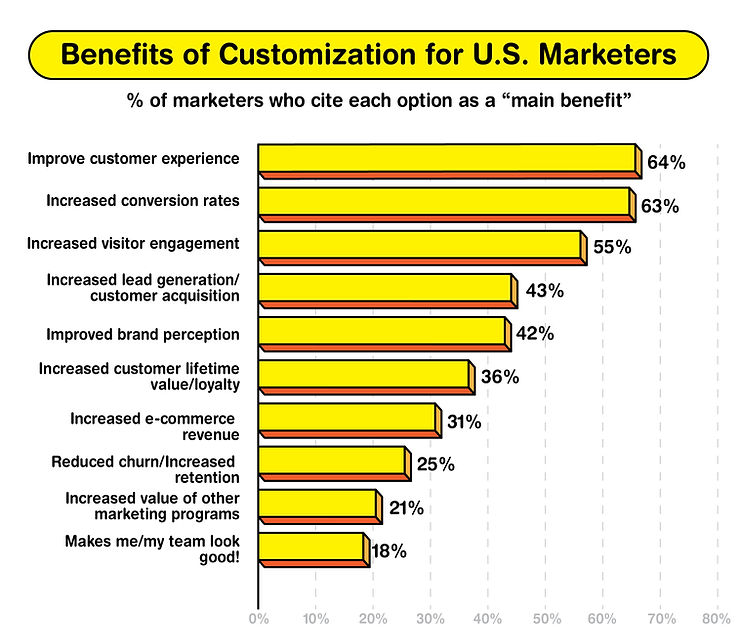
Consumer preferences are increasingly leaning towards personalization, with 80% of consumers preferring brands that offer personalized experiences. This trend underscores the importance of customization as a key differentiator for brands seeking to build loyalty.
Deloitte’s research further reinforces this trend, revealing that 36% of consumers show an interest in products and services tailored to their individual needs. This inclination towards personalization is even more pronounced among younger consumers, with 43% of 16-24 year-olds and 46% of 25-30 year-olds attracted to bespoke offerings. However, despite this clear demand for tailored experiences, there is a gap in the market, as only one in six consumers has actually engaged with personalized products or services.
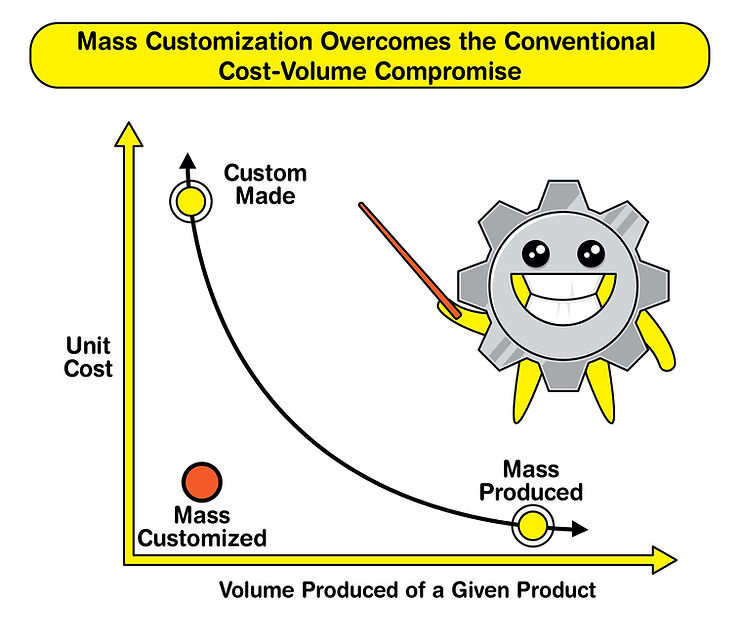
The chart shows how production volume affects unit cost. Historically, producing many units lowered the cost per unit, placing mass-produced items in the bottom right of the chart. Custom items, made in small quantities for specific needs, were costly, appearing in the top left.
Mass customization challenges this, offering unique products at high volumes without high costs. This approach offers more benefits than just savings. It also allows for quicker production, personalized products, reduced excess stock, improved design, flexible shipping, more options, and enhanced quality.
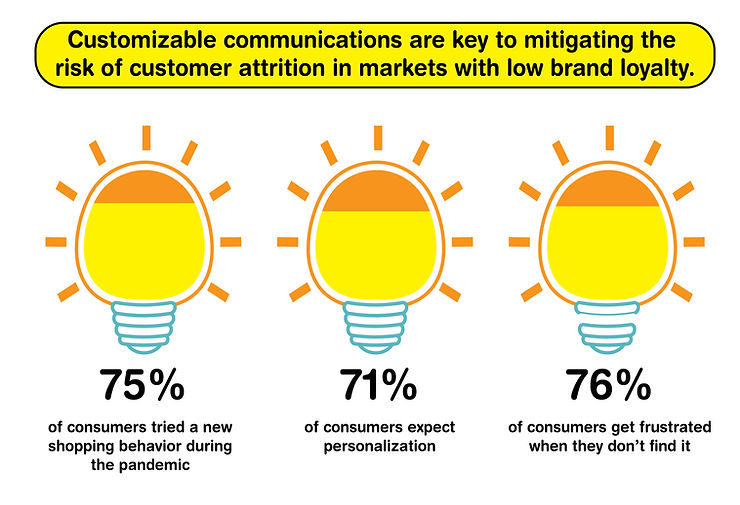
Not to mention, consumers increasingly demand personalized experiences, with 71% anticipating tailored interactions and 76% feeling frustrated when expectations aren’t met. The pandemic has intensified market fluidity, with 75% of consumers shifting to new stores, products, or purchasing methods when dissatisfied.
To bridge this gap, the industrial design industry is pivoting towards modular products that support the consumer’s craving for personalization. These products offer flexibility in customization, enabling users to modify or upgrade particular elements, thus providing a tailored experience without the necessity of purchasing entirely new items.
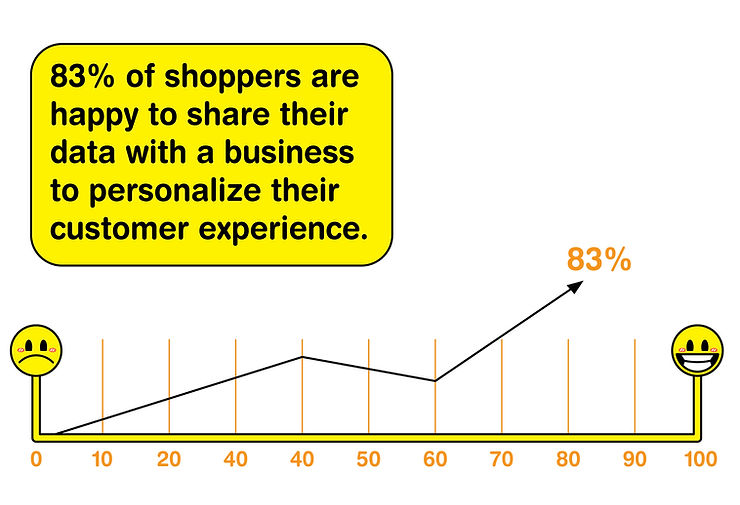
Cost-Efficiency in Manufacturing
Personalization in business is not just a buzzword; it’s a strategic investment that can significantly improve a company’s financials. According to Boston Consulting Group, businesses that master the art of personalization can see their growth rates soar by 6% to 10%, making it a vital component for competitive advantage and long-term profitability.
Furthermore, embracing personalization can have a profound impact on cost efficiency and revenue generation. Marketing strategies tailored to individual consumer preferences can slash customer acquisition costs by up to 50%, while potentially boosting revenue by 5 to 15% and increasing marketing return on investment by 10 to 30%. This personalized approach doesn’t just benefit the bottom line; it enhances customer satisfaction and outcomes, thereby reinforcing brand loyalty.
This trend is corroborated by data indicating that companies experiencing faster growth attribute 40% more of their revenue to personalized strategies compared to those with slower growth.
Eco-conscious Shift and Electronic Waste Reduction
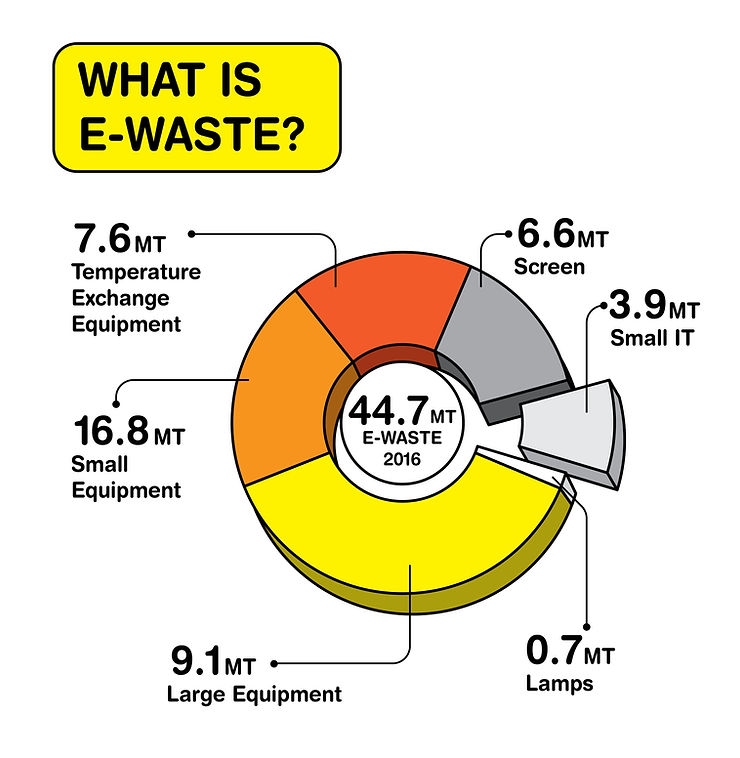
As consumer culture evolves, the environmental impact, particularly electronic waste, is becoming alarmingly clear. The UN’s Global E-waste Monitor reports a record 53.6 million metric tonnes of e-waste generated globally in 2019, an increase of 21% in five years.
In response, modular designs are emerging as a sustainable solution. Products engineered for easy upgrades minimize the need for complete replacements, significantly cutting down on the accumulation of electronic waste.
Potential Challenges and Rewards
Modular design in manufacturing is facing significant scrutiny with return logistics highlighting inefficiencies; consumer electronics companies report that merely 30% of returns costs are due to warranty issues, while the rest fall under administrative overhead, with non-defective products comprising 95% of returns.
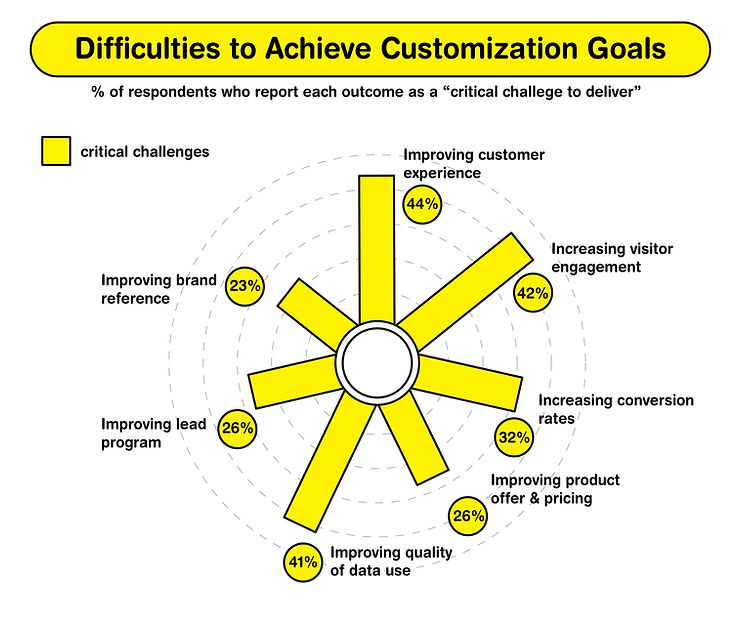
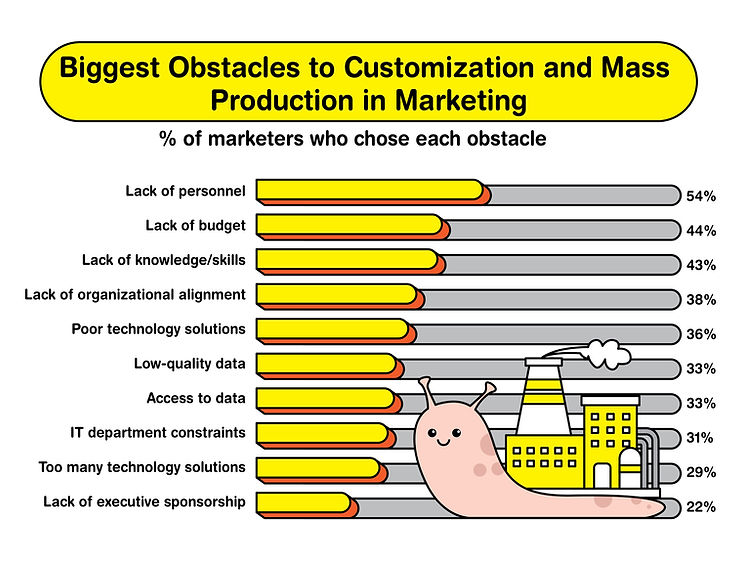
This design approach also encounters competitive challenges: 40% of manufacturers cite a lack of advanced technology and skilled workforce as obstacles, and 80% are operating without a full-scale supply chain planning solution, limiting their operational agility. Yet, the move towards modular design aligns with consumer values; 76% are attracted to ethically sourcing brands, 73% are willing to adjust their consumption for environmental benefits, and 46% would switch to an eco-friendlier brand. These figures indicate a growing market for manufacturers who prioritize ethical, sustainable practices in their design and production processes. Is Data-Driven Customization the Solution?
Collecting quality data stands at the forefront of overcoming the challenges associated with mass customization and modular design. It enables businesses to refine their product offerings and personalize customer interactions, ensuring each experience is as unique as the customer itself.
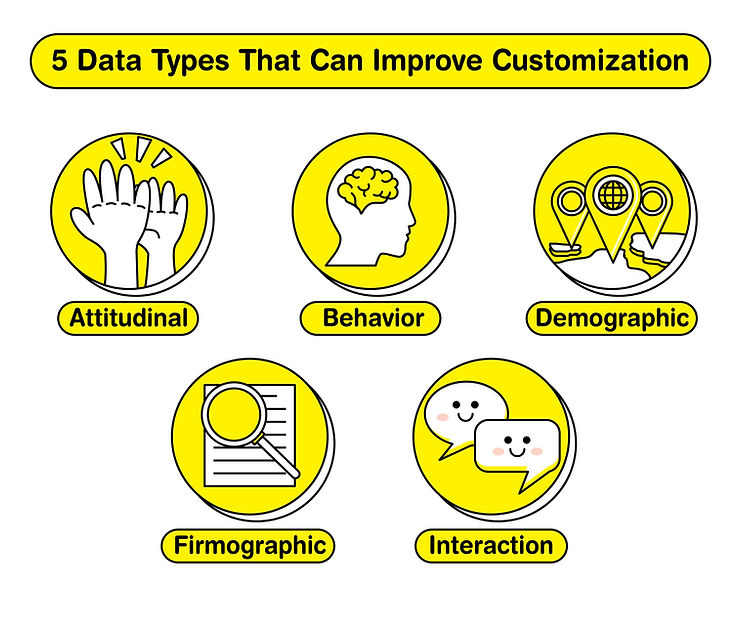
Enhancing Personalization through Data:
-
- Attitudinal Insights: Surveys and feedback mechanisms offer a window into customer opinions, guiding product innovation and refinement.
-
- Behavioral Trends: By studying the buying cycle, companies can uncover the reasons behind purchase decisions, allowing them to fine-tune strategies to reduce cart abandonment and facilitate a smoother purchase journey.
-
- Demographic Segmentation: Classifying customers by personal attributes such as age or income level helps in identifying market trends, enabling targeted and effective marketing strategies.
-
- Firmographic Analysis: Detailed knowledge about a potential business client’s industry and size empowers sales teams to tailor their pitch, increasing the likelihood of conversion.
-
- Interaction Metrics: Monitoring how customers interact with a company’s digital presence or customer service can highlight areas for improvement, leading to a better customer experience overall.
- Interaction Metrics: Monitoring how customers interact with a company’s digital presence or customer service can highlight areas for improvement, leading to a better customer experience overall.
By harnessing these types of data, companies can not only navigate but also excel in the realm of mass customization and modular design, crafting experiences and products that meet individual customer needs while maintaining efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion
The shift toward modular design is a strategic response to consumer demand for personalization and environmental responsibility. It challenges manufacturers to innovate while also offering a sustainable path to reduce e-waste and enhance customer loyalty. Success in this new era depends on a company’s ability to adapt, embrace technology, and invest in skills that align with evolving market values. Those who can navigate these changes stand to gain a competitive edge in a rapidly transforming industry.