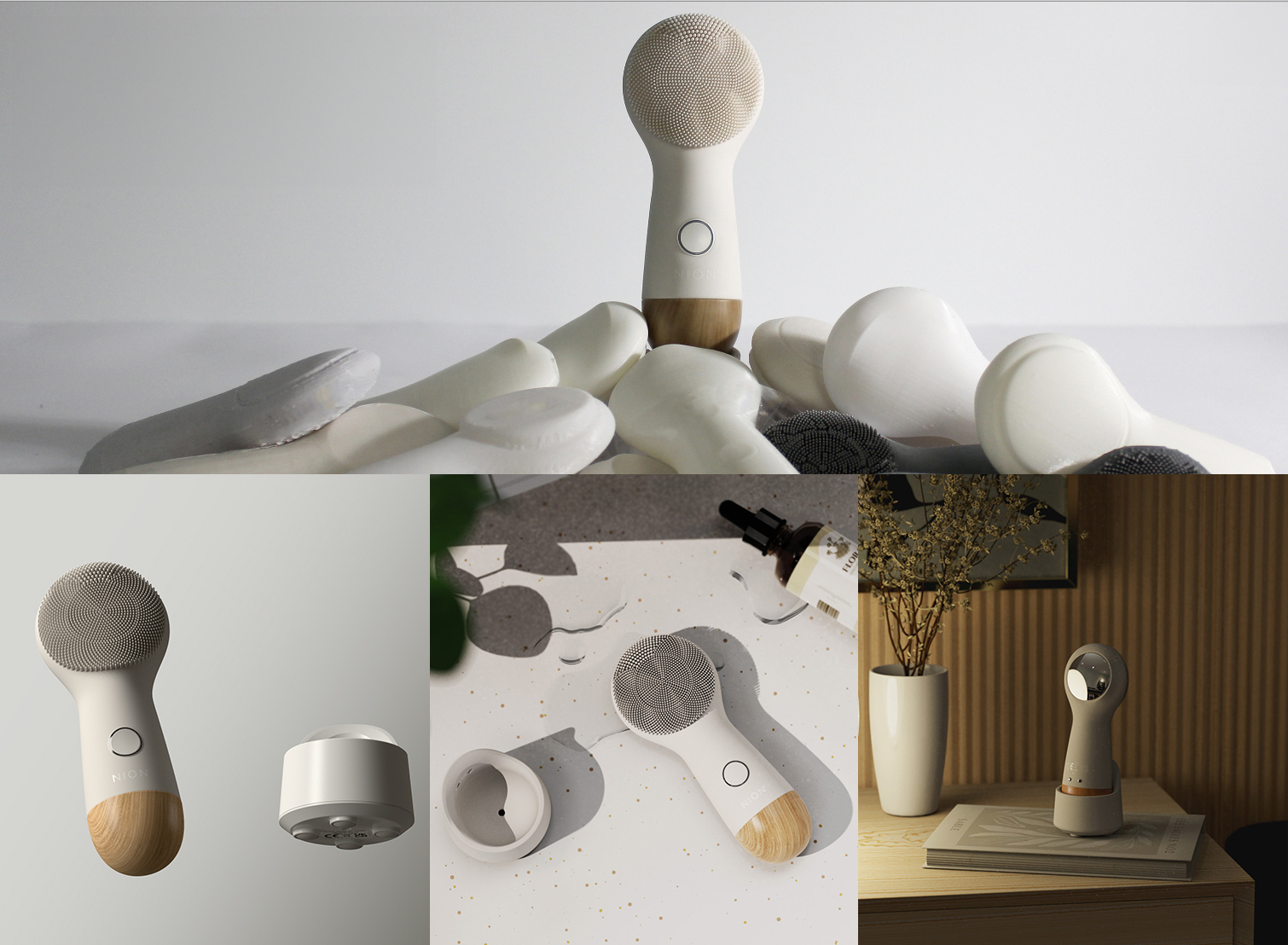
Low-Cost Alternatives to Injection Molding for Small-Volume Production
Many modern items, like kitchen tools, medical devices, toys, and household items, use plastics. If your company is a hardware startup, your product likely depends on plastic for its components.
Injection molding is a popular method for manufacturing plastic parts due to its efficiency and precision. However, the high upfront costs make it feasible only for large volumes. For small volume production or prototyping, injection molding is not the most cost-effective option.
For example, the total cost for a single injection mold can range from $5,000 to $100,000 depending on its complexity and size. Given these costs, finding low-cost alternatives to injection molding is crucial for small businesses and startups.
When developing a new product, startups face significant market uncertainty. Investing thousands of dollars in injection molding for an unproven product can be a risky move.
Here are some cheap options for injection molding services. These can help you make prototypes and small production runs. You won’t have to spend a lot of money.
Urethane Casting
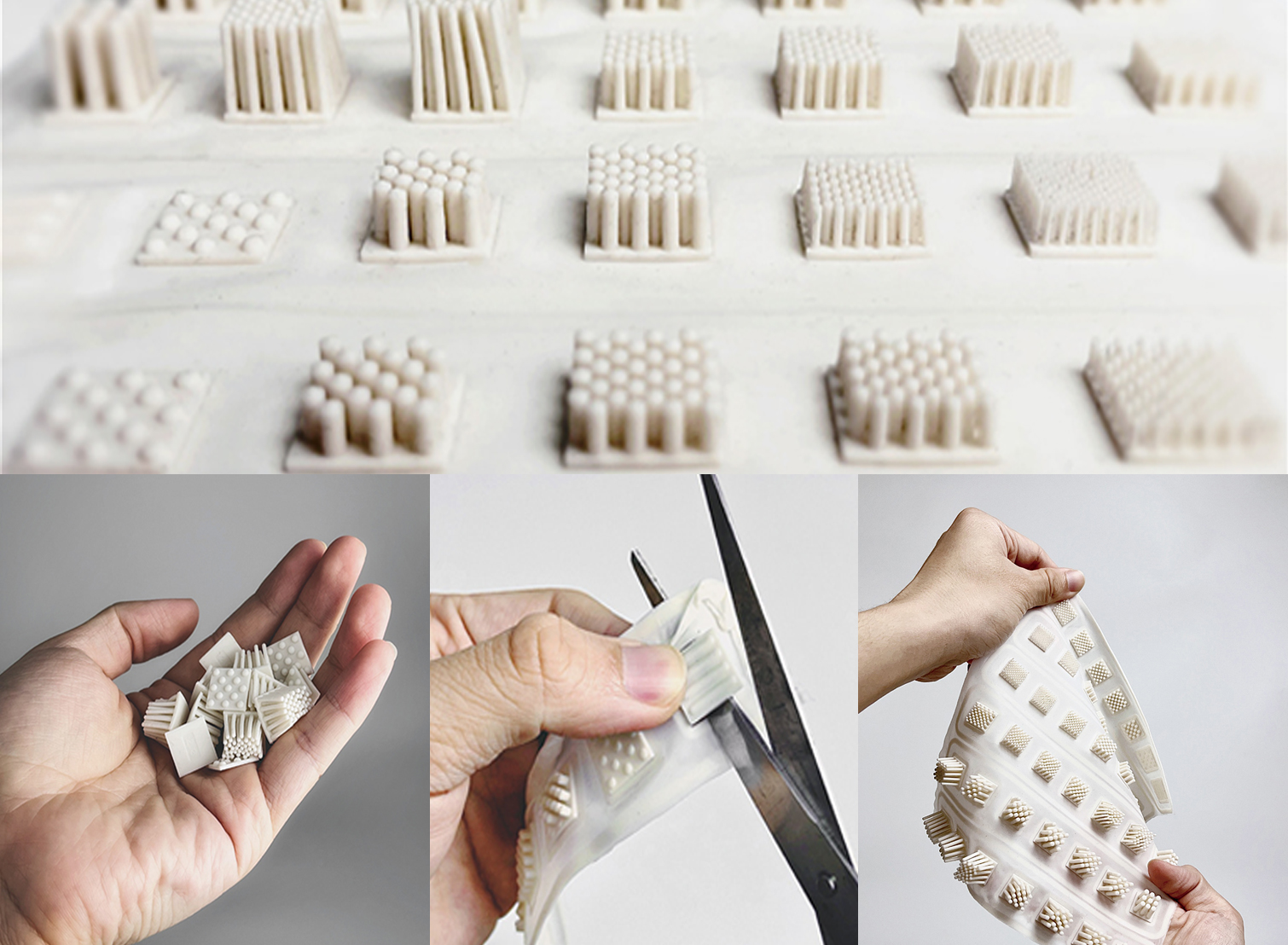
Urethane casting, also known as RTV Casting, Resin Casting, Vacuum Casting, or Silicone Molding, is a versatile alternative to injection molding.
Process: This method starts with creating a ‘master pattern’ using CNC Machining or high-resolution 3D Printing. Once the pattern is made, it’s used to create a urethane or silicone mold. This mold is then filled with a suitable resin to produce multiple copies of the product.
Materials and Quality: Urethane casting offers a wide range of resins that can mimic production-grade materials, from soft elastomers to hard plastics. This makes it a flexible choice for various production needs.
Applications: This process is ideal for cost-effective production runs of 20-200 parts, making it perfect for testing the market and gathering feedback from early adopters.
3D Printing
3D printing is a versatile and cost-effective method for prototyping and very low volume production. It requires no upfront investment in molds and can provide lead-times as short as a few hours.
Process: Various 3D printing technologies are available, including FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling), SLA (Stereolithography), and SLS (Selective Laser Sintering). Each technology has its own advantages and is suitable for different applications. The 3D printing market is expected to reach $34.8 billion by the end of 2024, highlighting its growing importance and application in manufacturing.
Surface Finish: 3D printed parts typically have a layered surface finish. Post-processing techniques such as sanding and painting can be used to achieve the desired surface quality.
Applications: 3D printing is ideal for quick iterations during the development process, creating appearance models, and producing marketing prototypes. This makes it a preferred choice for startups and small businesses.
Thermoforming
Thermoforming involves heating a plastic sheet and forming it over a mold to create various products. This method is straightforward and cost-effective.
Process: The process requires low pressure and temperature, allowing the use of inexpensive mold materials like plastic or wood. This makes thermoforming an accessible option for many manufacturers.
Applications: Thermoforming is ideal for simple products such as packaging trays, large panels, and dashboards. It is most commonly used in packaging, which accounts for 70% of its applications.
CNC Machining
CNC machining is a highly versatile manufacturing process that uses computer-controlled machines to cut and shape materials like plastics, metals, wood, and ceramics with exceptional precision.
Process: This method is renowned for its ability to achieve high tolerances and quick turnaround times. CNC machining involves the use of computer-aided design (CAD) software to guide the machines in creating detailed molds, dies, or patterns used in other manufacturing processes. The precision of CNC machining allows for tolerances as tight as ±0.005 inches.
Applications: CNC machining is ideal for low to mid-volume production runs, offering a fast and efficient way to produce accurate and high-quality parts. Its versatility and precision make it a go-to choice for a wide range of industries, from aerospace and automotive to medical and consumer products. This method is especially beneficial for projects that require rapid prototyping or production of parts with complex geometries.
3D Printed Molds
Using 3D printed molds is an innovative alternative to traditional metal molds in injection molding, offering significant cost and time savings.
Process: Advancements in 3D printing technology have greatly improved the quality and surface finish of 3D printed molds. These molds are created using high-resolution 3D printers, which allow for intricate designs and detailed features. As a result, 3D printed molds can achieve comparable quality to traditional metal molds but at a fraction of the cost and time.
Applications: This method is particularly suitable for testing production-grade materials in low quantities. It provides an efficient way to validate designs and production processes before committing to the expense of metal molds. According to Stratasys, “3D printed molds can reduce lead times by up to 90%”. This significant reduction in lead time makes 3D printed molds an attractive option for rapid prototyping and short-run manufacturing.
Low-Cost Injection Molding
Low-cost injection molding is achieved by using less expensive materials for molds, such as aluminum instead of steel.
Process: This approach involves creating molds from lower quality steel or aluminum, which significantly reduces the initial tooling costs. Aluminum molds are easier and faster to machine compared to steel molds, which further lowers production expenses and shortens lead times.
Applications: Low-cost injection molding is ideal for small volume production runs with simpler part designs. It offers a cost-effective solution for startups and small businesses looking to produce limited quantities without the high upfront costs typically associated with traditional injection molding. Using aluminum molds can reduce tooling costs by up to 90%. This makes it an attractive option for companies aiming to bring products to market quickly and affordably.
Rotational Molding
Rotational molding is a versatile method used to create large, hollow parts by heating a mold filled with material and slowly rotating it.
Process: In rotational molding, operators put material in a hot mold and rotate it on two axes. The material rotates slowly to coat the walls of the mold evenly, creating a hollow part as it cools and hardens.
Applications: This method is ideal for producing large, hollow parts such as tanks, containers, and playground equipment. It is particularly useful for creating complex shapes and seamless parts without the need for additional assembly. Rotational molding is often 10-20% cheaper than other molding methods for producing hollow parts. This cost efficiency makes it a preferred choice for manufacturers looking to produce durable, hollow parts at a lower cost.
Compression Molding
Compression molding is a process where material is placed into a heated mold and then compressed to form a part.
Process: In compression molding, a pre-measured amount of material is placed into an open, heated mold. The mold is then closed and pressure is applied, forcing the material to conform to the shape of the mold. The material is cured under heat and pressure until it solidifies into the desired part.
Applications: This method is suitable for producing large, fairly intricate parts such as automotive components, electrical housings, and appliance parts. Compression molding is particularly advantageous for high-strength, lightweight parts. Compression molding can reduce material waste by 5-10% compared to injection molding. This efficiency in material usage makes it a cost-effective option for manufacturing intricate parts.
Injection Molding with 3D Printed Inserts
Using 3D printed inserts in traditional injection molds is an innovative method to reduce costs and improve efficiency. This approach leverages the precision and flexibility of 3D printing to create custom inserts that fit into standard injection molds.
Process: 3D printed inserts allow manufacturers to quickly and cost-effectively test new designs. The inserts can be produced in a fraction of the time compared to traditional methods and are easily replaceable, making them ideal for iterative design processes.
Applications: This method is particularly suitable for rapid prototyping and short production runs. It enables manufacturers to produce small batches of parts with production-grade materials without the high costs associated with traditional mold-making. Using 3D printed inserts can reduce mold production time by up to 85%.
Cold Casting
Cold casting is a technique where metal powders are mixed with a liquid resin and then poured into a mold. This process allows for the creation of parts that look and feel like metal without the need for high-temperature metal casting processes.
Process: The mixture of metal powders and resin is poured into a mold, where it is allowed to cure and solidify. This results in a part that has a metal-like finish and properties, providing a cost-effective alternative to traditional metal casting.
Applications: Cold casting is suitable for creating metal-like parts, including sculptures, prototypes, and decorative items, without the need for expensive and energy-intensive metal casting methods. It is particularly useful for projects that require the appearance and feel of metal at a lower cost. Cold casting can achieve metal-like finishes at a fraction of the cost of true metal casting.
Next Steps: Recommendations from Our Team
Having explored ten potential alternatives to injection molding, here are our tailored recommendations to guide your decision-making process
Recommendations for Prototyping and Low-Volume Production
3D Printing
3D printing is a versatile and efficient method for rapid prototyping and low-volume production runs. It allows for quick design iterations and is ideal for creating complex geometries that would be challenging with traditional manufacturing methods.
This technology supports various materials, including plastics, metals, and resins, providing flexibility in the types of parts that can be produced. Additionally, 3D printing enables the production of functional prototypes that can be tested and validated before moving to large-scale production.
3D Printed Molds
Using 3D printed molds is a cost-effective solution for low-volume production. These molds can be produced quickly and used to create small batches of parts, typically up to 100 units.
They are particularly useful for testing and validating designs, as they allow for rapid changes without the high costs associated with traditional mold-making processes. This approach is suitable for producing parts in materials such as silicone, urethane, and low-melting-point metals.
Urethane Casting
Urethane casting is an effective method for producing parts in volumes ranging from 20 to 200 units. It involves creating a master pattern, typically using 3D printing, which is then used to produce silicone molds.
Urethane casting provides high-quality parts with excellent surface finish and material properties similar to injection-molded parts. This method is ideal for producing functional prototypes, small production runs, and bridge manufacturing before committing to high-volume production.
Recommendations for Specific Part Types
Thermoforming
Thermoforming is a highly efficient method for producing simple, large, or hollow parts. It involves heating a plastic sheet until it becomes pliable, then forming it over a mold using vacuum or pressure. Many manufacturers often use this method to produce packaging, panels, and large hollow parts such as car parts, appliance housings, and custom trays.
Thermoforming offers low tooling costs and quick turnaround times, making it suitable for both prototyping and low to mid-volume production.
Rotational Molding
Rotational molding is ideal for producing large, hollow parts with uniform wall thickness and stress-free structures. This process involves placing powdered plastic in a mold, which is then heated and rotated biaxially.
The plastic melts and coats the interior of the mold, forming the part. Rotational molding is commonly used for tanks, containers, playground equipment, and outdoor furniture. It offers cost-effective tooling and the ability to produce large, durable parts with complex shapes.
Recommendations for Precision and Versatility
CNC Machining
CNC machining is a highly precise manufacturing method suitable for low to mid-volume production runs. It involves using computer-controlled machines to remove material from a solid block (workpiece) to create the desired shape. CNC machining is capable of producing parts with tight tolerances and excellent surface finishes in a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. This method is ideal for producing high-precision components for industries such as aerospace, medical devices, and automotive.
Recommendations for Durable, Production-Grade Parts
Low-Cost Injection Molding
Low-cost injection molding using aluminum molds is an excellent option for producing durable, production-grade parts in high volumes. Aluminum molds are less expensive and faster to manufacture than steel molds, making them suitable for simpler designs and shorter production runs. Injection molding provides consistent part quality, fine detail, and the ability to use a wide range of thermoplastics. This method is widely used in industries such as consumer electronics, automotive, and medical devices.
Compression Molding
Compression molding is beneficial for producing high-strength parts with minimal material waste. This process involves placing a preheated material, typically a thermoset plastic or composite, into a heated mold cavity. The mold is then closed, and pressure is applied to form the part.
Compression molding is ideal for manufacturing composite parts, gaskets, and high-performance components that require durability and excellent mechanical properties. It is commonly used in the automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors.
Recommendations for Metal-Like Finishes
Cold Casting
Cold casting is an excellent choice for creating decorative and prototype parts with a metal-like appearance. This process involves mixing metal powders, such as bronze, aluminum, or copper, with resins to create a material that mimics the look and feel of metal. Cold casting is cost-effective and can produce parts with intricate details and a high-quality finish. It is ideal for creating sculptures, architectural elements, and decorative hardware.
Choosing the Right Method
Each manufacturing method has unique strengths and is best suited to specific needs and production requirements. Consulting with a manufacturing expert can help determine the most appropriate method for your project. For personalized recommendations and further guidance, feel free to contact Gizmospring. Our team can provide expert advice to ensure your project meets its goals in terms of quality, cost, and timeline.
Conclusion
Finding low-cost alternatives to injection molding is crucial for small volume production, helping to reduce costs and improve efficiency. By evaluating these alternatives, businesses can choose the best method based on their specific needs, costs, and production requirements. Engineering and manufacturing professionals play a vital role in guiding product development decisions, ensuring that the chosen processes meet quality and cost-efficiency standards. Exploring these alternatives can lead to significant benefits, from reduced lead times to enhanced flexibility in design and production.
Have more questions?
We’ve outlined ten alternative solutions to injection molding. If you’d like personalized recommendations for your project, our team at Gizmospring is here to help! Feel free to reach out to us at info@gizmospring.com for expert advice and support tailored to your needs.