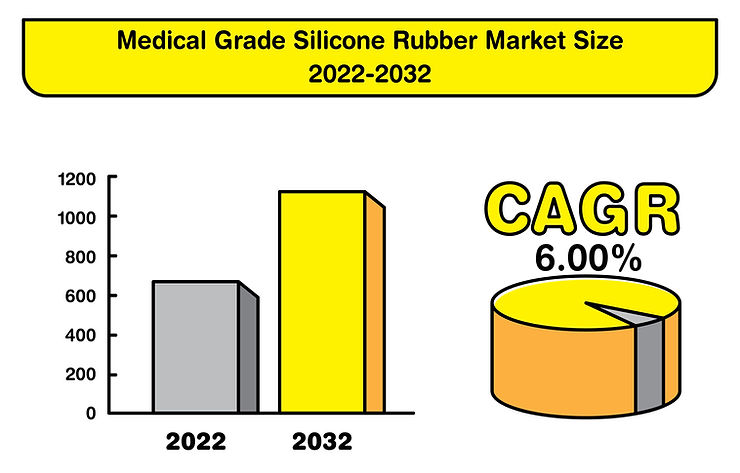
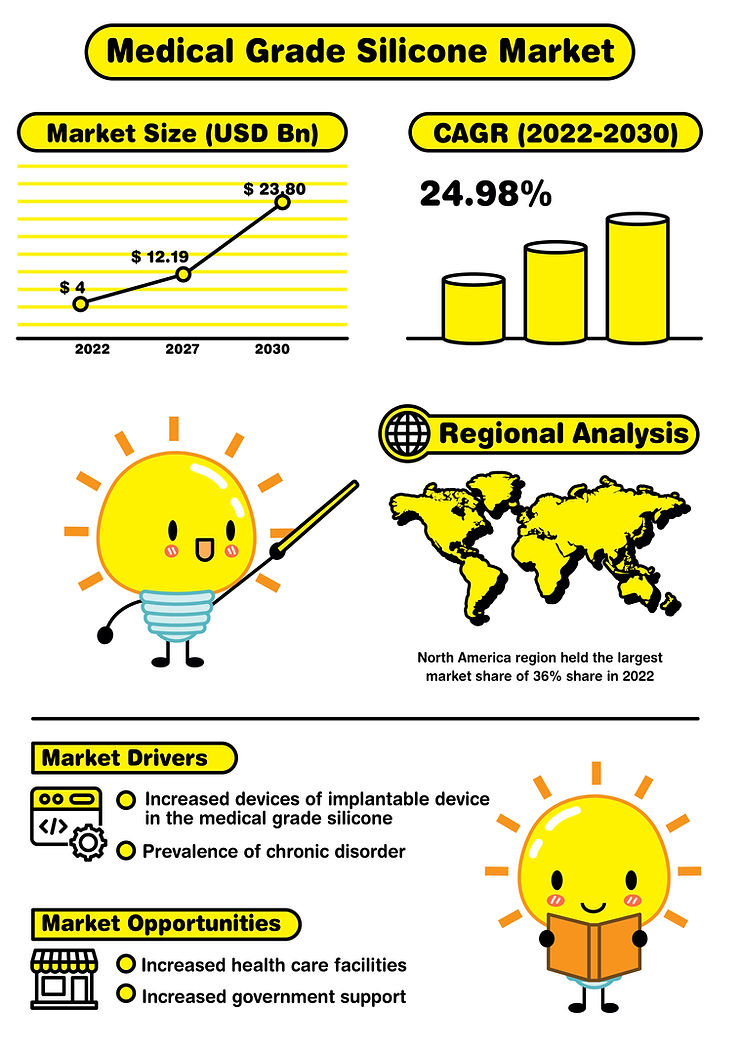
The medical-grade silicone market is rapidly expanding. In 2022, it held a value of over USD 4 billion, but by 2030, projections indicate it could soar to an impressive USD 23.8 billion. This represents a remarkable growth rate of 24.98% between 2022 and 2030. The adaptability and safety of medical-grade silicone position it as a preferred choice for a host of innovative medical instruments and devices.
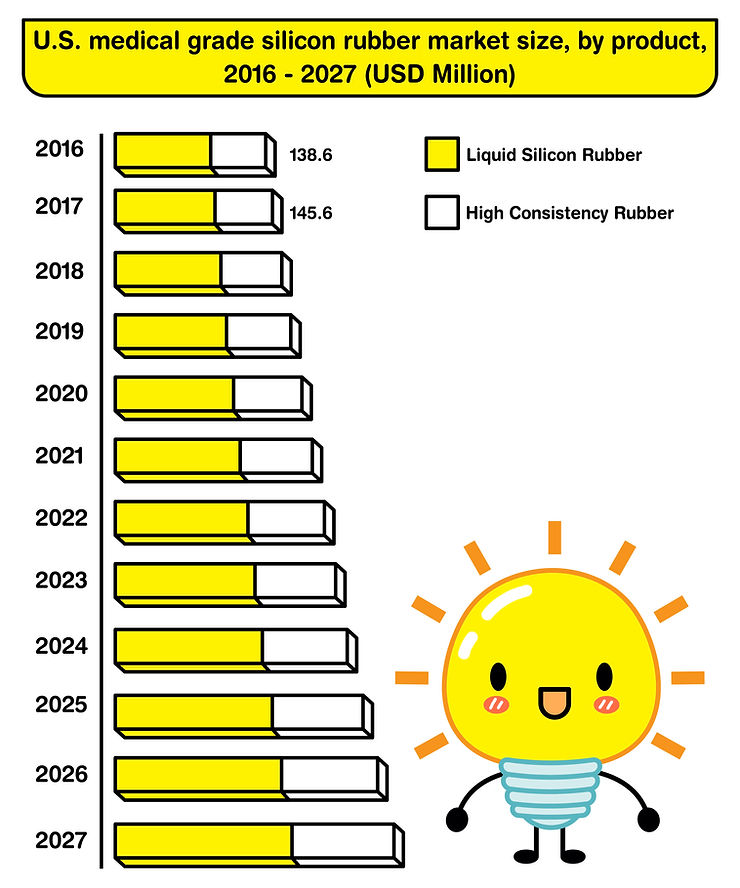
As global healthcare expenditure is expected to increase by 5.7% each year, will the use of reliable materials like medical-grade silicone become more important?
Our discussion will cover:
- Decoding medical-grade silicone
- Why All the Buzz Around Medical Grade Silicone?
- Spotlight: MedTech Innovations Harnessing Silicone
- Deep Dive: Manufacturing Process of Medical Grade Silicone
- The Underlying Importance of Manufacturing Excellence
- Medical Silicone Manufacturing: The Future of Med/Health Tech
- Choosing the Right Manufacturing Partner: Key Considerations
Decoding medical-grade silicone Silicone Overview:
- Synthetic polymer is known for flexibility, water resistance, and biocompatibility.
- Used across various industries.
- ‘Medical Grade Silicone’ is specially tested and deemed safe for medical use.
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Highlights:
- Considered a superior form of traditional silicone.
- Ultra-pure, with high biocompatibility—safe for use in the human body.
- The fluid nature allows for precise molding.
- Durable and maintains stability under different conditions.
- Can be sterilized without degradation.
- Resistant to high temperatures.
- Resists bacteria and other pathogens.
Implications for MedTech:
- Ideal for creating intricate medical parts.
- Suitable for devices in direct contact with the body.
- Potential for use in implants and wearable tech, enhancing safety and effectiveness.
Why All the Buzz Around Medical Grade Silicone?

Medtech industries have developed more than 500,000 distinct medical devices. These range from wearable items like skin patches and insulin pumps, to implanted devices such as pacemakers, and even include stationary equipment like home monitoring systems. In almost every interaction with the healthcare system, a patient comes into contact with equipment made from this material, underscoring its widespread significance.
But what’s behind this rising demand? A few key drivers:
Healthcare Spending: The global expenditure on healthcare has seen a sharp uptick. More people are prioritizing their health and are willing to spend on advanced medical treatments.
Technological Advancements: The MedTech arena is bursting with new inventions and tools, and many of these innovations rely on medical-grade silicone for its unique properties.
Aging Population: An increase in the senior demographic means more medical products and interventions. Silicone’s biocompatibility makes it an ideal choice for this demographic.
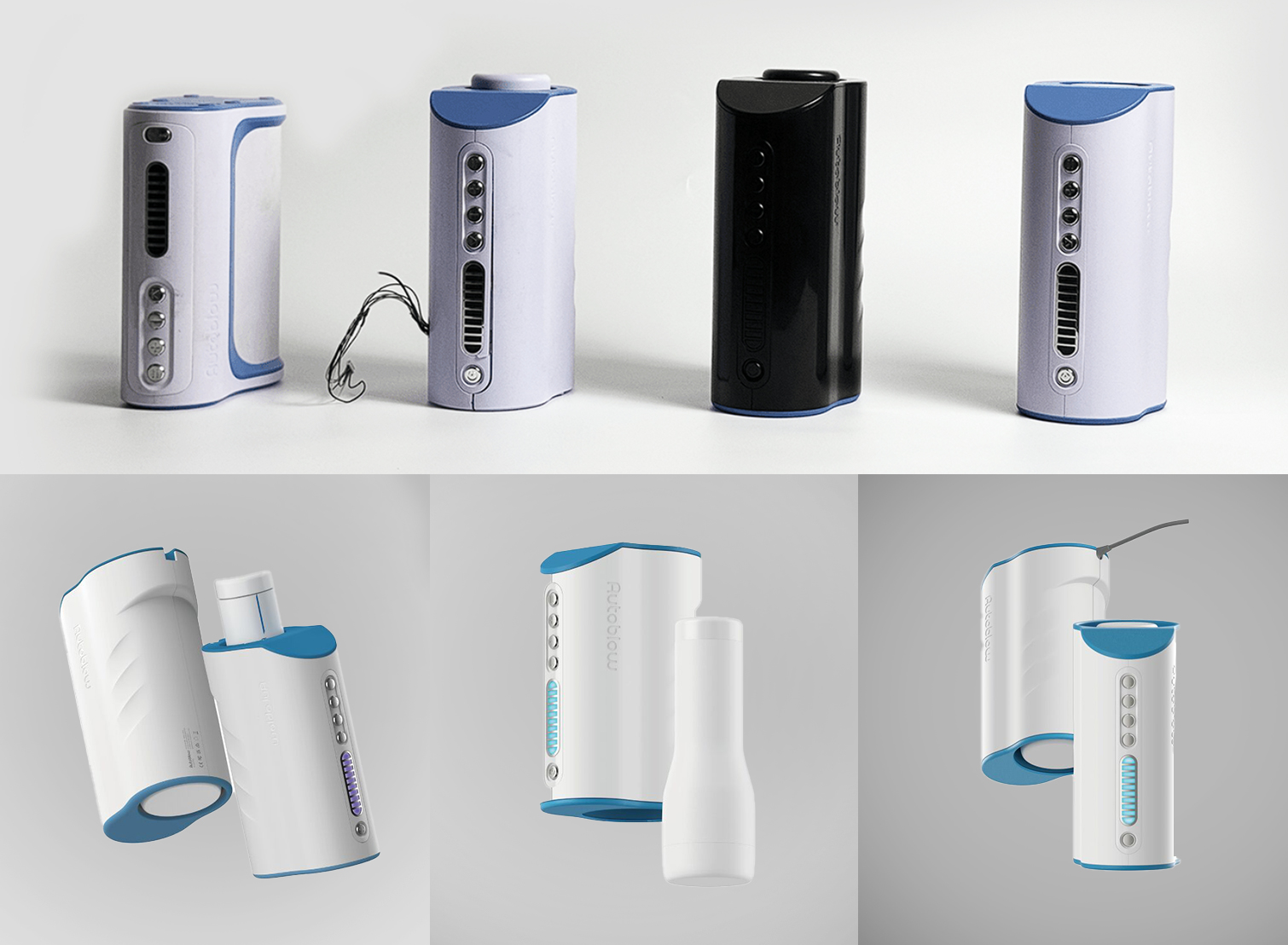
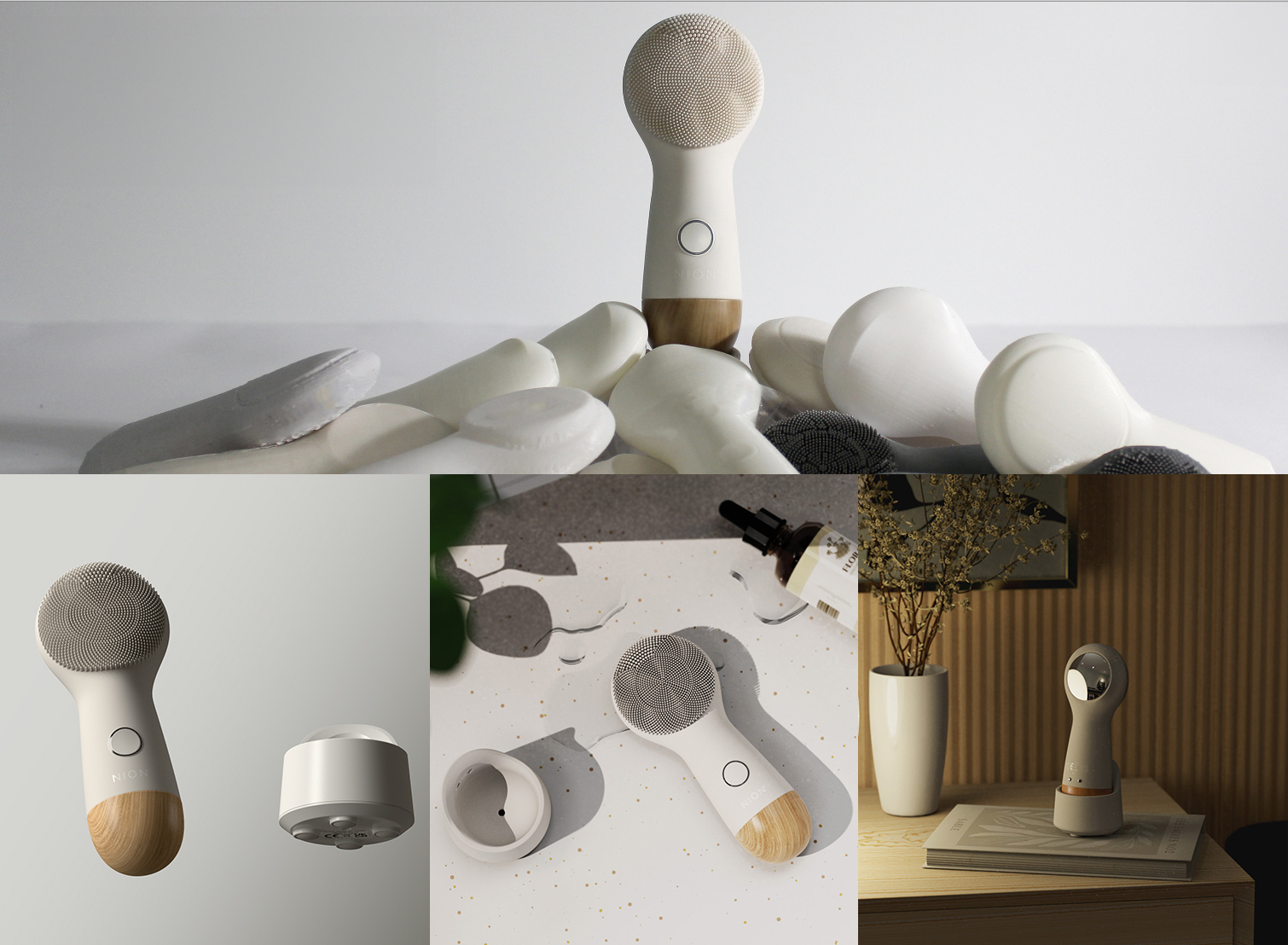
Spotlight: MedTech Innovations Harnessing Silicone
So how has medical silicone made life better for us?
Cochlear Implants
Role: These advanced devices restore hearing for those with significant hearing impairments.
Why Silicone? Its biocompatibility ensures long-lasting implants and prioritizes patient safety.
Catheters and Tubes
Role: Essential for various medical procedures.
Why Silicone? With its inherent antimicrobial traits, silicone helps reduce of infections.
Wearable Medical Devices
Role: Devices like smart patches keep track of vitals, while insulin pumps regulate diabetes.
Why Silicone? Known for its skin-friendliness, silicone also boosts the lifespan of these devices.
Deep Dive: Manufacturing Process of Medical Grade Silicone
How is medical-grade silicone manufactured, and how do we ensure its quality?
Raw Material Verification
- Objective: Ensure quality. Each batch of raw material for medical-grade silicone undergoes testing for purity.
- Significance: Contamination can affect the silicone’s biocompatibility. For example, a 2017 recall of catheters by a prominent medical equipment provider highlighted the importance of raw material checks.
Compounding
- Procedure: In controlled settings, silicone elastomer is combined with catalysts, fillers, and pigments to suit specific medical applications.
- Outcome: The process allows neonatal medical devices to be suitable for premature infants, while surgical instruments are made durable.
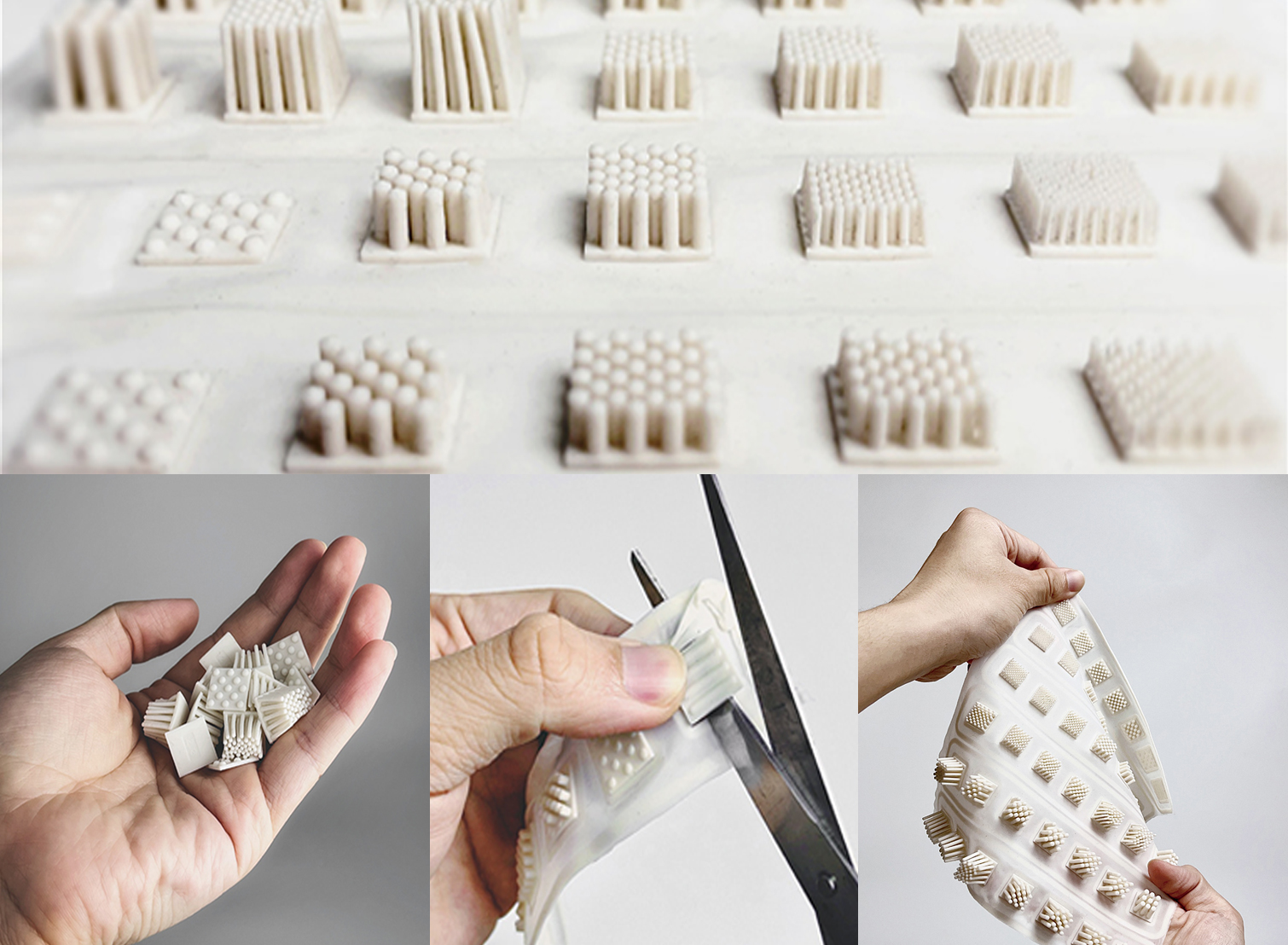
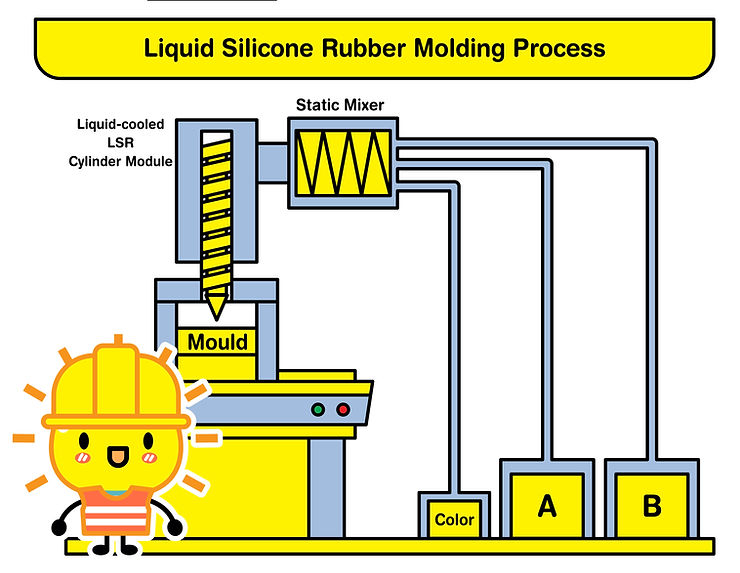
Molding
- Method: Medical components are primarily produced using Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) injection molding due to its accuracy. The silicone mixture is injected into a heated mold.
- Application: The LSR method was essential for producing specific respiratory valves during the 2020 pandemic.
Post-Curing
- Step: After molding, parts are heated further to enhance their strength and longevity.
Quality Control and Testing
- Checks: Adhering to FDA guidelines, each production batch undergoes tests, including biocompatibility, tensile strength, and sterilization effectiveness.
- Relevance: Studies, such as one by the National Library of Medicine, indicated that consistent quality checks reduced medical device-related incidents in recent years.
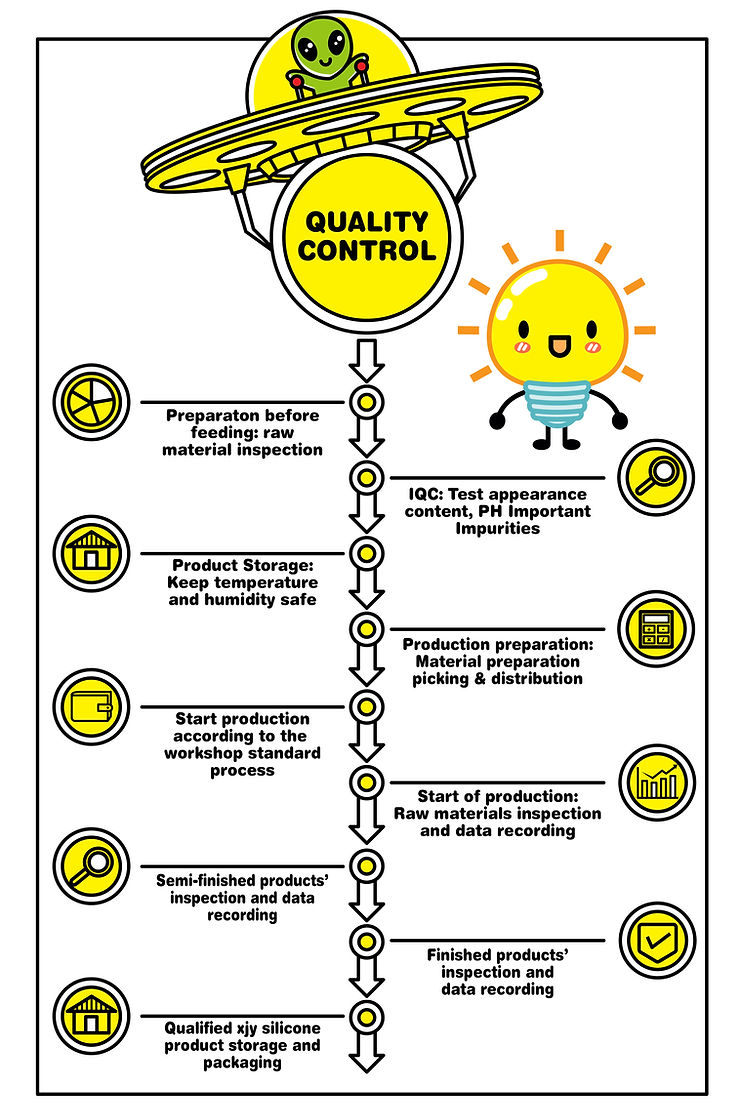
Hence, it is clear that understanding the process of quality control (QC) is crucial to ensuring product consistency and safety.
The Underlying Importance of Manufacturing Excellence
Patient Safety: Patient safety is the cornerstone of medical product design and manufacturing. Achieving impeccable biocompatibility and ensuring the structural integrity of every product is vital in reducing potential health risks.
Durability and Performance: From pacemakers to joint replacements, medical devices and implants are often intended to serve patients over extended periods. Excellence in manufacturing is critical to ensuring these products remain reliable, providing both longevity and consistent performance.
Regulatory Adherence: Securing certifications like ISO 13485 is not just about ticking a box. This specific standard relates to the quality management system requirements for medical device production and signifies a manufacturer’s commitment to global best practices. Adhering to such rigorous standards is crucial for building and maintaining trust in a brand, especially in the sensitive realm of medical products.
Economic Considerations: Efficient manufacturing impacts the bottom line, reducing waste and preventing costly recalls. But it’s more than just numbers; it’s about maintaining brand integrity in the eyes of stakeholders and the public.
Medical Silicone Manufacturing: The Future of Med/Health Tech
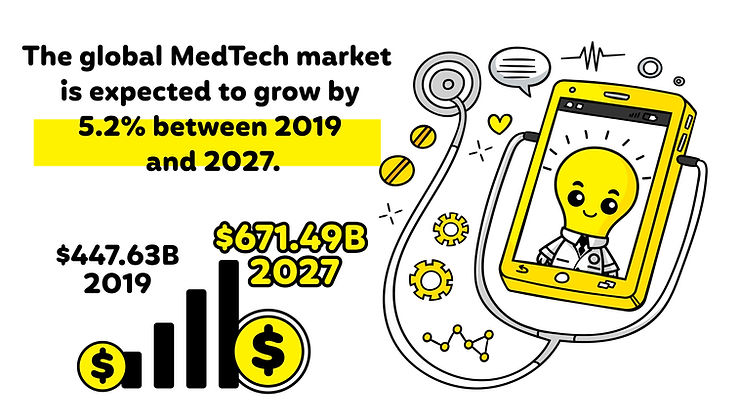
Precision Manufacturing:
Medical devices are getting more detailed. This means making silicone parts needs to be very accurate, using advanced tools and strong quality checks.
Scalability:
There’s a growing need for more silicone-based medical devices. Producers must be ready to make more, faster. This might mean using machines more, having bigger places to work, or refining how they work.
Material Innovations:
There’s ongoing research to improve medical silicone. Producers should be aware of new findings to make better, longer-lasting devices.
Regulatory Compliance:
The medical industry has strict rules. Producers must always meet these rules, which could mean more checks, earning certain badges, or following international guidelines.
Advanced Testing and QC:
Checking the quality of products is very important. Producers might use new ways to test, like computer models or watching closely during making, to make sure everything’s right.
Customization and Personalization:
With new technologies like 3D printing, there’s interest in more personalized medical items. Producers should be ready to make unique items in small numbers without losing quality or speed.
Sustainability:
Making things in a way that’s good for the environment is becoming more important. This could mean using cleaner methods, less waste, or looking into recycling used silicone.
Integration of Electronics:
Medical devices are getting smarter. This means producers might need to put electronic parts into silicone devices, requiring a mix of skills.
Supply Chain Management:
There’s a growing global need for medical silicone devices. Managing where materials come from and ensuring they’re good and always available is important.
Collaborative R&D:
To keep up with medical technology, producers might work more with researchers, tech companies, or hospitals. Working together can lead to quicker and better innovations.
Choosing the Right Manufacturing Partner: Key Considerations

- Certifications in Manufacturing: Certifications are more than just labels. They show that a manufacturer is dedicated. Certified groups tend to have fewer product problems and recalls.
- Looking Beyond Certifications: Certifications are important, but they don’t tell everything about a manufacturer. Companies should also consider their history, skills, and methods.
- Benefits of DFM Partnership: Partnering with a Design for Manufacturability (DFM) group can help find and solve problems early. This can save companies money by making the production process smoother.
- Reputation and Quality: A brand’s image is linked to the quality and safety of what they make. In MedTech, having to recall a product can hurt a brand and be costly. Good manufacturing practices can help avoid these problems.
- Competing in MedTech: Being slightly better in terms of safety and product quality can give a big advantage in the market. With the MedTech industry growing steadily, having high-quality products is key to staying ahead.
Therefore, choosing the right MedTech manufacturing partner is not just about certifications. It’s also about skills, working efficiently, and keeping a good brand image in a busy market.