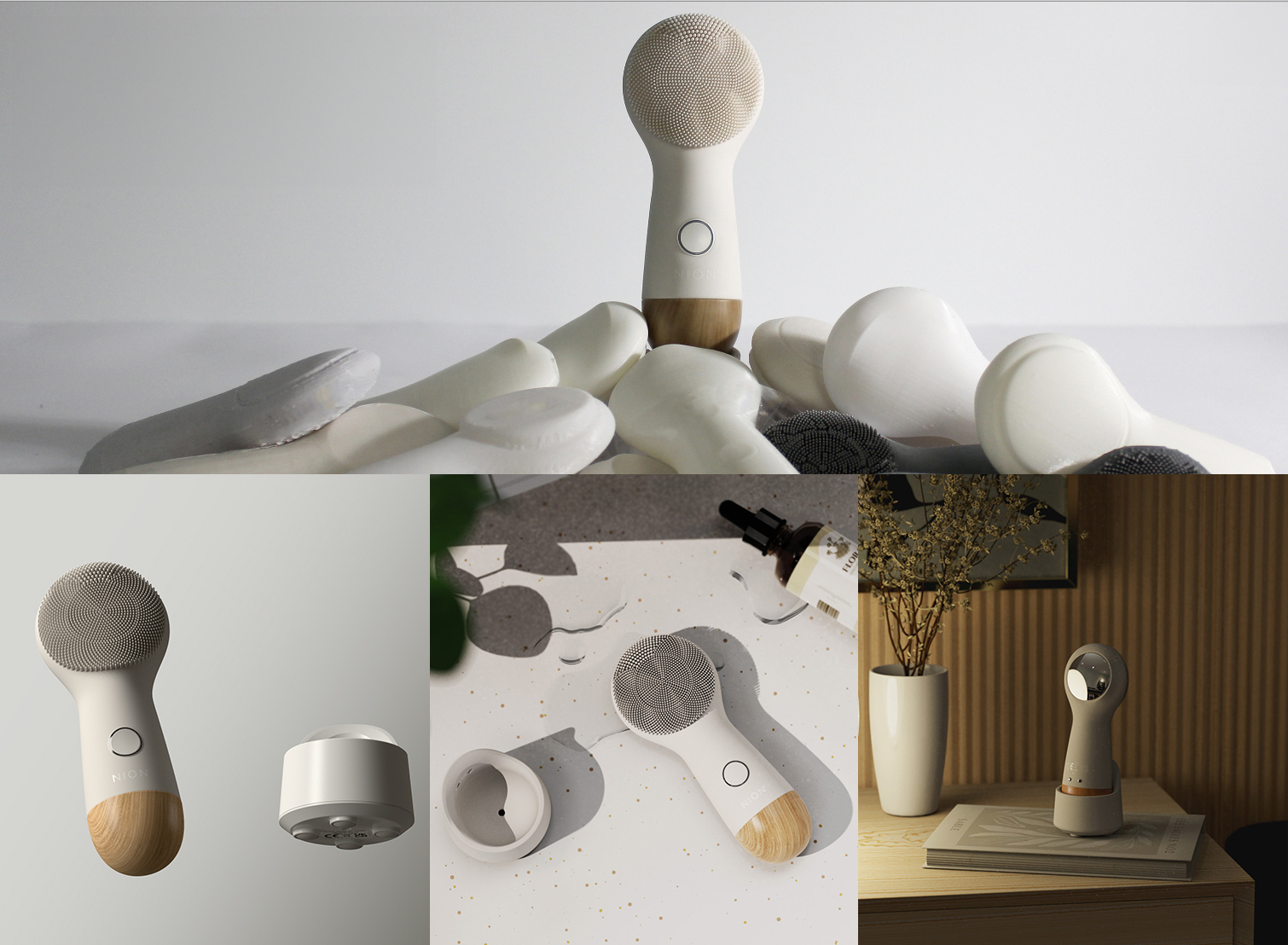
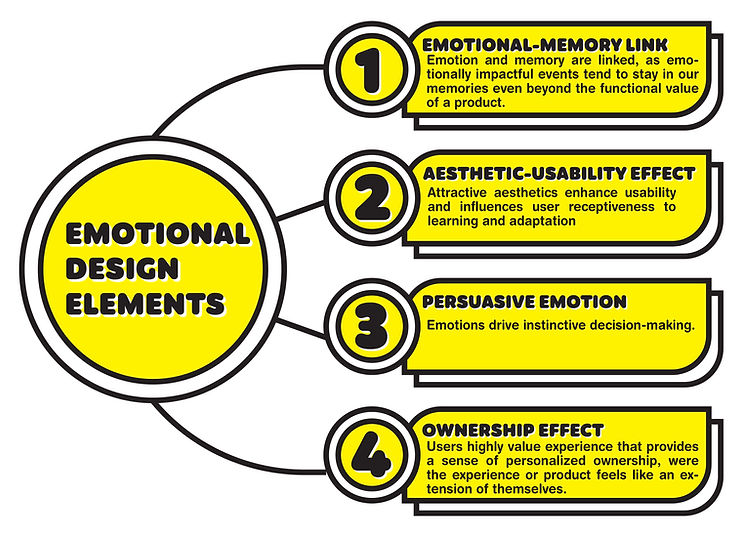
Ask any design expert about the importance of emotion in product design and they will tell you that it’s an incredibly powerful tool. In fact, research shows that emotionally-driven reactions occur approximately 3,000 times faster than rational thought. This is because the emotional region of the brain, the amygdala, processes sensory input five times more rapidly than rational thought. When you understand this, it’s no surprise that 95% of consumer purchases are influenced by the subconscious mind. Virtually any product can evoke an emotional response, which is why so much time and effort is invested in good product research and development. If a product can elicit a response from a user, a deeper intangible value can be manifested. Whether it’s for an everyday home appliance or a personalized wearable device, good design is key to genuine and long-term customer fulfillment. In this article, we will cover:
- What Is Emotional Design?
- Why Should We Consider Emotional Design In The Manufacturing Process?
- 3 Criteria For Emotional Design To Work
- How To Apply Emotion-Driven Innovation in The Product Design Process?
- Unveiling the Future of Emotional Design
What is emotional design?
At its core, emotional design is a captivating concept that strives to build profound connections between users and products, transcending mere functionality and aesthetics. As highlighted in Don Norman’s book “Emotional Design: Why We Love (or Hate) Everyday Things,” emotional design involves intentionally integrating elements and features into product design to evoke specific emotional responses from users. By recognizing the significance of emotions, emotional design acknowledges their profound impact on user satisfaction and engagement, allowing for a more meaningful and fulfilling product experience.
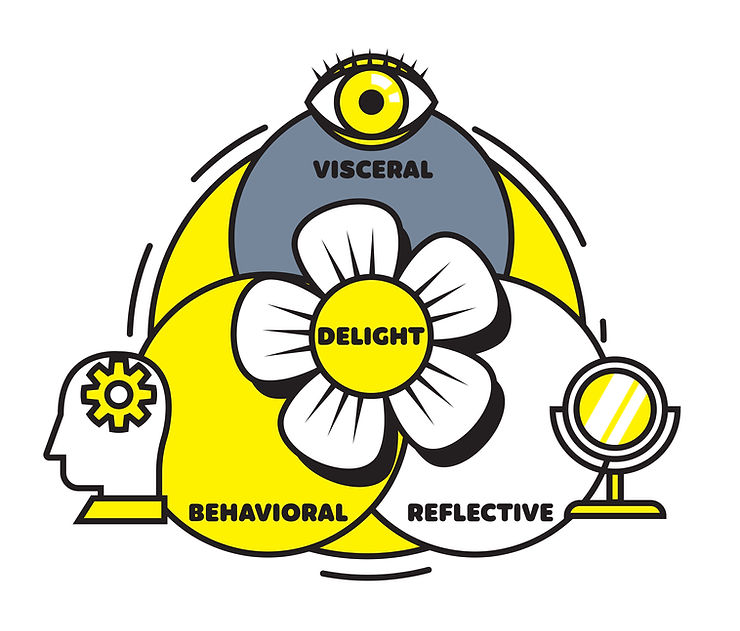
Visceral Emotional Design:
- A visceral reaction sets the initial mood and frames the overall experience.
- Powerful visceral reactions have benefits like setting a positive context, forgiving faults, and encouraging positive socialization.
- Playful onboarding and motion design can evoke visceral reactions.
Behavioral Emotional Design:
- Behavioral reactions reflect our immersion in the product experience.
- Positive behavioral reactions empower users, build trust, and encourage repeat engagement.
- Behavioral design focuses on usability, function, performance, and effectiveness.
Reflective Emotional Design:
- Reflective reactions determine how we feel after the experience.
- Positive reflective reactions promote sharing, create a sense of pride, and have cultural impact.
- Reflective emotional design captures meaning, thoughts, shareability, and cultural influence.
Why Should We Consider Emotional Design In The Manufacturing Process? In today’s competitive market, emotional design is practically imperative to distinguish products and accomplish business objectives. By incorporating emotional design elements into the design process, companies can develop unique and memorable experiences that set their offerings apart from the competition. This differentiation not only captures customers’ attention but also influences their purchasing decisions, ultimately driving return on investment (ROI) for the business.
Three Criteria For Emotional Design To Work
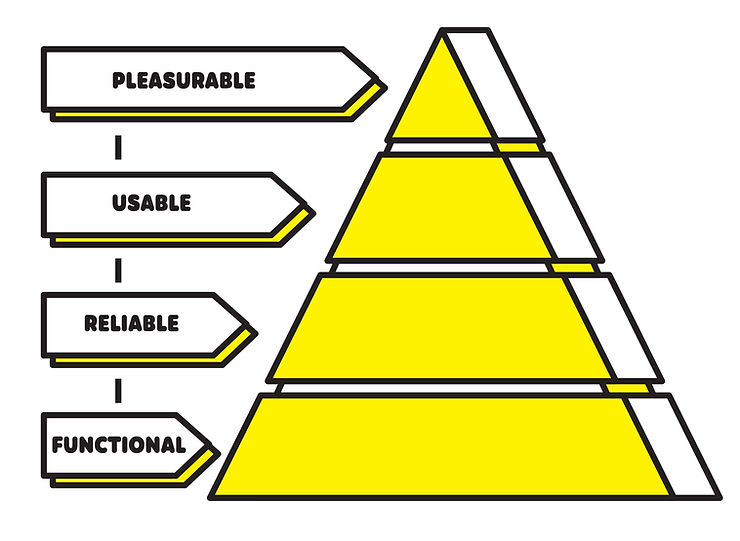
Before considering Emotional Design in a product, it is essential to ensure that the basic user needs are met. According to Aaron Walter’s hierarchy of user needs, the first criterion is functionality, where the product must solve a problem, satisfy a need, or provide clear value to users. Without a compelling reason to use the product, the emotional aspect alone cannot create a meaningful experience. The second criterion is reliability, which refers to the product working as expected based on common conventions, without unpleasant surprises. Reliability builds trust and confidence in the product, establishing a solid foundation for the emotional elements to flourish.
The third criterion is usability, ensuring that the product offers an intuitive and effortless user experience. A well-designed interface reduces cognitive effort and allows users to navigate and utilize the product seamlessly. Usability is crucial for users to engage with the product smoothly and sets the stage for emotional design elements to enhance the overall experience. It is crucial to understand that meeting the foundational needs of functionality, reliability, and usability is a prerequisite for satisfying higher-level user needs, such as joy or delight.
How To Apply Emotion-Driven Innovation in The Product Design Process?
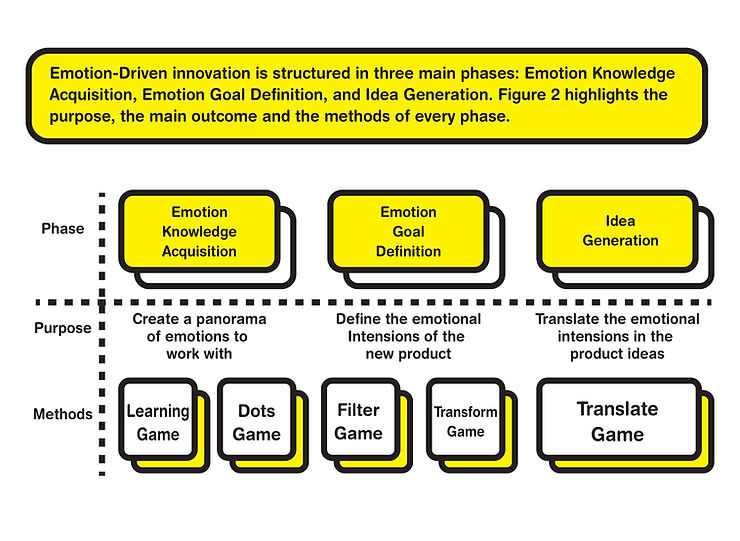
Emotion-Driven Innovation follows a structured process consisting of three main phases: Emotion Knowledge Acquisition, Emotion Goal Definition, and Idea Generation. These phases aim to acquire emotional knowledge, define emotional intentions, and generate emotion-focused product ideas, respectively.
- Emotion Knowledge Acquisition: In this phase, the team develops emotional granularity by discussing personal emotional experiences evoked by products. The “Learning Game” and “Dots Game” methods are used to create a panorama of emotions related to the new product.
- Emotion Goal Definition: This phase focuses on defining the emotional intentions of the new product. The “Filter Game” method helps select specific emotions for the product’s emotional strategy, while the “Transform Game” method transforms these emotions into a product design brief using Human-Product Interactions (HPIs).
- Idea Generation: The objective of this phase is to translate emotional intentions into emotion-focused product ideas. The “Translate Game” method supports this process, emphasizing the development of strong and meaningful ideas rather than generating a large quantity.
Unveiling the Future of Emotional Design
The future of emotional design is poised for innovation and connection. Advancing technology will amplify emotional resonance in products beyond functionality. By utilizing data analytics and AI we can refine designs based on evolving emotional preferences. For instance, collaborations between experts and users can yield human-centric experiences, while products adapting to emotions will become the norm. This era will seamlessly integrate technology and emotions, reshaping our device interactions and relationships. Embracing emotional design’s potential, we forge empathetic connections between humans and technology.